- AI Fire
- Posts
- ✈️ This Is How You Put Your Ambitions On Autopilot With AI
✈️ This Is How You Put Your Ambitions On Autopilot With AI
Gain a serious competitive edge for 2025. This piece details the strategies for deploying AI agents to manage tasks, optimize your website, and scale your work.

📊 What's your current experience with AI Agents? |
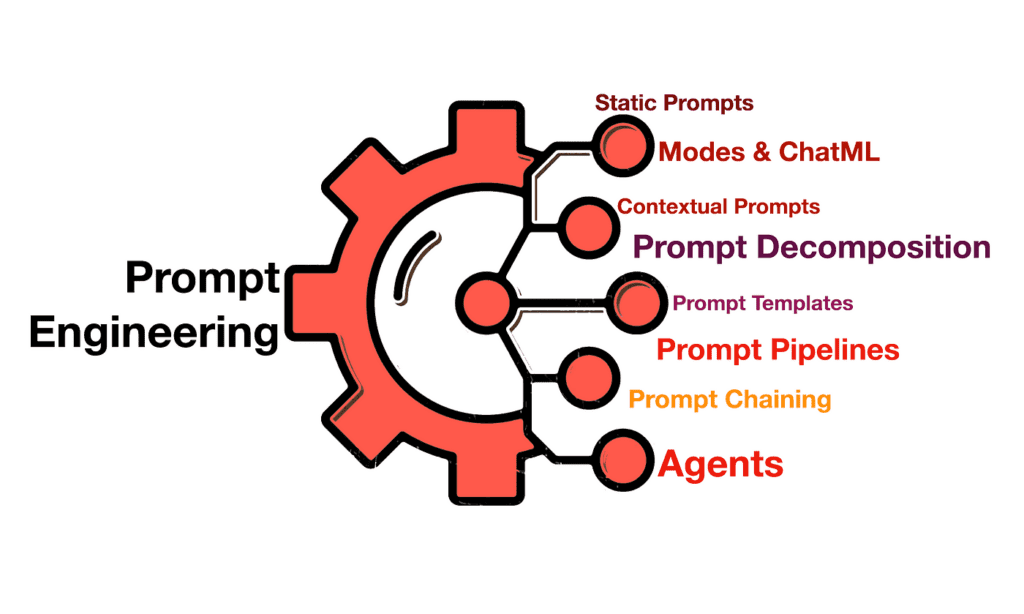
Table of Contents
We are officially living in the era of Artificial Intelligence Agents (AI Agents) - a time when artificial intelligence doesn't just answer questions but actually acts on your behalf. This is no longer science fiction; it is a reality that is reshaping how we work, do business, and interact with the digital world. This complete guide will walk you through everything you need to know to master AI Agents in 2025, based on real-world testing and practical examples that will forever change how you think about automation.
What Are AI Agents And Why Are They The Future?
To understand the power of AI Agents, we need to take a step back in evolution. Traditional AI models like ChatGPT initially acted as brilliant "brains" in a box. You could ask them questions, debate with them, and have them generate text or images, but they couldn't act in the digital world. They were confined to their chat interface.

AI Agents have shattered that barrier. They represent a massive paradigm shift: from responsive AI to proactive AI.
An AI Agent, in essence, is an autonomous system that can perceive its environment, make plans, make decisions, and execute actions to achieve a specific goal. Think of them as digital assistants given "hands" and "eyes" - specifically, control over a virtual keyboard and mouse - to interact with a computer exactly like a human does.
The major breakthrough came when platforms like OpenAI began implementing "agent" modes, allowing users to create virtual computers that the AI could control to browse websites, fill out forms, click buttons, and complete complex real-world tasks without human intervention.
Why should you care?

Exponential Efficiency: An AI Agent can work 24/7, simultaneously handling multiple repetitive tasks that humans often find tedious and time-consuming.
New Accessibility: They can access and synthesize information from behind login pages, proprietary databases, and complex systems that normal APIs cannot reach.
Deep Automation: We are no longer just automating individual tasks (like sending an email), but entire workflows that involve multiple steps and multiple applications.
Competitive Advantage: The individuals and businesses who master this technology first will have an unparalleled advantage in speed, scalability, and innovation.
This isn't theoretical. People are already using these agents to order goods, send connection messages on LinkedIn, create videos in bulk, and conduct deep market research that previously would have taken weeks to complete. The revolution is here.
Step 1: Getting Started With Your First Real-World Task – Automated Purchasing
One of the best ways to see the power of an AI Agent is to give it a specific, real-world task. Making a purchase is a perfect example because it involves multiple steps: searching, comparing, selecting, and checking out.
Setting Up The Agent Environment
The process typically works as follows:
Select Agent Mode: In your chosen AI platform, activate the agent function (sometimes called "browse mode" or "computer control").

Give Clear Instructions: This is the most critical step. Instead of a vague command, be extremely specific. For example, instead of
"buy me some shoes,"try: "Search the Adidas Vietnam website for a pair of men's running shoes in black, size 42, from the Ultraboost line, priced under 3,500,000 VND. Add it to the cart and proceed to the checkout page."
Watch the Virtual Computer: The system will spin up a virtual computer environment, usually a browser window. You will see the mouse cursor move, text being typed into search fields, and websites being navigated automatically. This is the agent "at work."

Provide Additional Details: A smart agent will recognize missing information. It might ask back, "There are several black Ultraboost versions. Would you like the Light version or the 1.0 version?" This interaction demonstrates its reasoning and problem-solving capabilities.

Monitor the Process: Observe how the agent navigates the site, filters products, and adds items to the cart. This is a valuable learning opportunity to understand how the agent "thinks" and how to write better prompts in the future.

Important Safety And Security Considerations
This is an area where caution is paramount. When it comes to payments, adhere to these golden rules:
Never Share Credit Card Information: Absolutely never provide your full credit/debit card details for the agent to auto-fill. These systems are still new, and the security risks are real.

Use Safer Payment Methods: Instruct the agent to proceed to the final step and generate a payment QR code. You can then scan the QR code yourself with your phone to complete the transaction. This way, the agent does all the tedious work, but you retain final control over the payment. Services like PayPal, where you can log in and authenticate manually, are also a good option.

Review Before Approving: A well-designed agent will always present you with a final summary before executing an irreversible action (like placing an order). Always double-check this summary carefully.
Common Challenges And Solutions

Captcha Barriers: Most current AI Agents are programmed to respect captcha systems. When faced with an "I'm not a robot" test, it will pause and request human intervention. This is a safety feature, not a bug.
Website Compatibility: Not all websites are built in a way that is friendly to automation. Sites with complex structures, heavy use of dynamic JavaScript, or non-standard interface elements can be challenging for an agent. If the agent fails, try a different website or simplify the task.
Prompt Precision: This is the biggest challenge. A vague prompt like "find me a birthday gift" will lead to unpredictable results. Always be as specific as possible: the recipient, budget, interests, preferred websites, etc.
Learn How to Make AI Work For You!
Transform your AI skills with the AI Fire Academy Premium Plan - FREE for 14 days! Gain instant access to 500+ AI workflows, advanced tutorials, exclusive case studies and unbeatable discounts. No risks, cancel anytime.
Step 2: Automating Professional Social Media Outreach
AI Agents excel at professional networking tasks, especially on platforms like LinkedIn. They can help you expand your network, find potential clients, or recruit talent efficiently.
LinkedIn Automation Strategy
Here is how to set up an automated outreach workflow on LinkedIn responsibly:
Create a Test Account: The number one rule of automation: never experiment on your main account. Create a secondary LinkedIn account to test and refine your prompts. This helps you avoid embarrassing mistakes that could impact your professional reputation.

Define Your Target Audience: Be highly specific. Instead of
"find managers,"command it: "Using LinkedIn Sales Navigator, search for 'Marketing Managers' who work at software development companies in Vietnam with a company size of 201-500 employees."

Craft Personalized Messages: This is where AI Agents truly shine. You can ask it to do more than send a template message. Try this prompt:
"For each profile found, visit their 'Recent Activity' section. If they have shared an article, start the message by complimenting that article. If not, mention a recent achievement of their company. Then, briefly introduce that I am a conversion rate optimization specialist and ask if they would be interested in receiving a free analysis of their website."

Set Clear Limits: This is critically important to avoid runaway automation. Always end your prompt with a stopping condition. For example:
"Execute this process for exactly 10 people and then stop. Report the results in a table including Name, Title, Company Name, and the message content that was sent."
Monitor and Optimize: Track the response rate. If it's low, adjust your message, targeting criteria, or approach. Automation is an iterative process.

Critical Prompt Engineering Tips

The power of AI Agents comes with significant responsibility. A poorly written prompt can lead to disastrous consequences:
Messaging the wrong people.
Sending inappropriate or repetitive content.
Creating awkward situations that damage your personal or business brand.
Always include stopping conditions and negative constraints in your prompts. For example, "...contact 15 people, but do not contact anyone who works at company X, Y, or Z."
Step 3: Understanding The New SEO Landscape
The rise of AI Agents is creating an entirely new field we can call Agent Engine Optimization (AEO). This is fundamentally different from traditional SEO because agents do not "browse" the web like humans do.
How AI Agents Change Search Behavior
When an agent searches for information, it operates on logic and efficiency, not intuition or aesthetics.

Literal Decisions: Agents interpret meta descriptions literally. If your description says "A step-by-step guide to installing XYZ," an agent will prioritize it over a vague description like "Discover the power of XYZ."
Different Link Choices: Humans might judge a website's quality based on design, branding, or general feel. Agents cannot. They will prioritize links with clear anchor text, clean URL structures, and other technical signals.
Absolute Priority on Speed: A website that is a few seconds slow might annoy a human. For an agent executing hundreds of tasks, that delay is unacceptable. Slow-loading sites will be abandoned without mercy.
Following Specific Instructions: You can actually "command" agents through your meta tags. For example, a description like: "This article contains tabular data. Agents can directly extract the table with ID '#data-table-2025' for the most accurate results" can guide the agent on how to collect information efficiently.
Optimizing Your Website For AI Agent Traffic
To attract and effectively serve AI Agents, focus on the following elements:
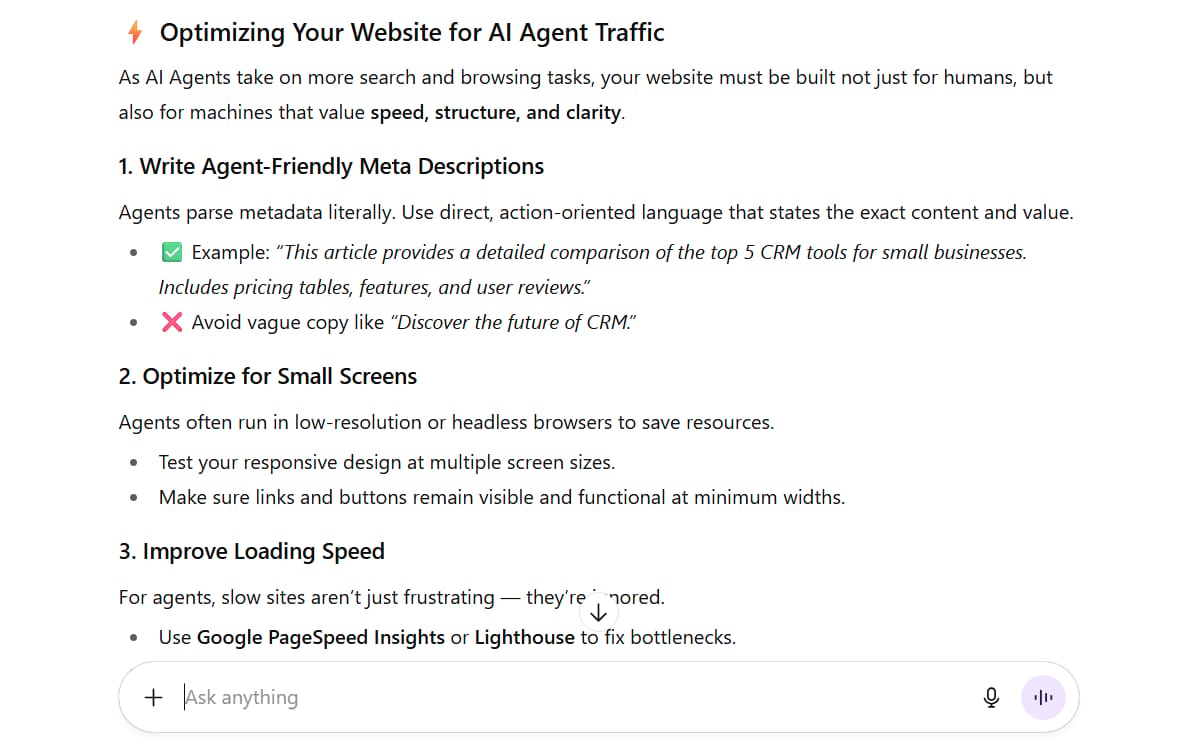
Write Agent-Friendly Meta Descriptions: Use direct, action-oriented language. Clearly state the page's content and the value it provides. Example: "This article provides a detailed comparison of the top 5 CRM tools for small businesses. Includes pricing tables, features, and user reviews."
Optimize for Small Screens: Agents often run in low-resolution virtual browsers to save resources. Ensure your responsive design works perfectly on small screens, with buttons and links that are large and easy to click by coordinates.
Improve Loading Speed: Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to optimize every aspect of your site. Speed is no longer just a ranking factor; it's a basic requirement to even be considered by an agent.
Use Large, Clear Buttons: Agents navigate based on coordinates and DOM selectors. Buttons with clear IDs, large sizes, and proper spacing are much easier for an agent to interact with reliably.
Implement a Reading Mode: Providing a simple, text-only version of your content (similar to Safari's "Reader View") can help agents extract information much faster without being distracted by ads or complex interface elements.
The Rise Of Personal SEO
AI Agents are making personal branding more important than ever. When someone commands their agent, "Find me the top motion graphic designers in Vietnam" or "List the VFX experts experienced with Unreal Engine," you want to appear in those results.
This means:
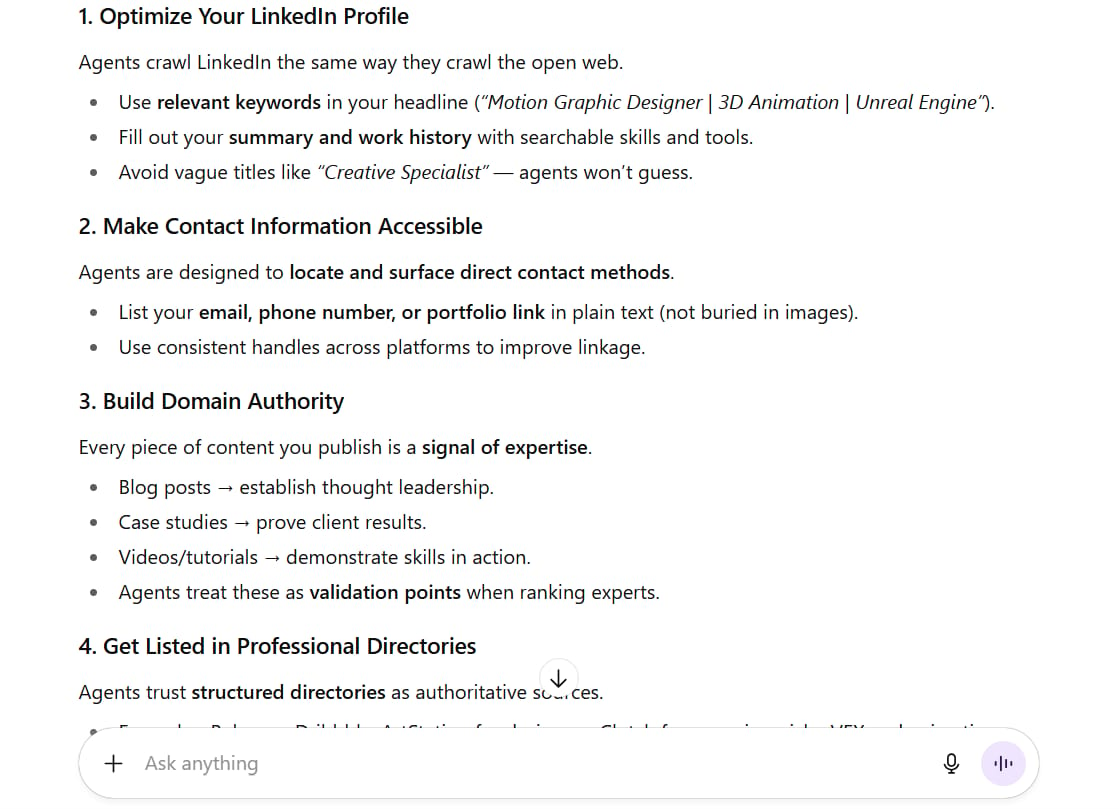
Optimizing Your LinkedIn Profile: Use relevant keywords in your headline, summary, and work experience sections.
Making Contact Information Accessible: Clearly include your phone number, email, or other direct contact methods. Agents are designed to find this information.
Building Domain Authority: Create content (blog posts, case studies, videos) that showcases your expertise. Each piece of content is a data point for agents to validate your expertise.
Getting Listed in Professional Directories: Ensure your profile exists on reputable industry-specific websites and directories.
Step 4: Building Automated Content Creation Systems
AI Agents can automate complex content creation workflows, turning ideas into finished products without constant human intervention.
Automated Video Creation Workflow
Imagine a fully automated daily news video creation process:
Define Content Parameters: Start with a prompt:
"Every morning at 8:00 AM, create a 2-minute video summarizing the top 3 technology news stories from TechCrunch and The Verge. The video should have a fast, dynamic style with English subtitles."

News Aggregation: The agent will visit the specified websites, scan the headlines and intros of the latest articles, and identify the three most important stories based on predefined criteria (e.g., comment count, media coverage).

Script Generation: Based on the gathered information, a large language model (LLM) will write a concise video script for each story.

Visual Assembly: The agent will then use tools like Python's MoviePy library or video service APIs to combine the script (converted to AI voiceover) with relevant stock images or video clips. It could be instructed to search for royalty-free visuals on sites like Pexels or Unsplash.

Output and Distribution: The final video is compiled and can be uploaded to a Google Drive folder or even published directly to a test YouTube channel.
The "Software On The Fly" Concept

What's revolutionary here is that the agent isn't just using software. In many cases, it creates temporary scripts or applications to complete a specific task and then discards them. For example, to create the video, the agent might write a short Python script using MoviePy, run it to generate the MP4 file, and then delete the script.
This represents a shift from permanent software solutions to task-specific, disposable applications created on demand. This is incredibly efficient and flexible.
Quality Expectations And Limitations

It's important to be realistic. The output quality of these current automated systems often resembles basic slideshows rather than professionally produced videos. However, their value lies not in artistic perfection, but in:
Speed: The ability to generate dozens of content variations in minutes for A/B testing.
Scale: Consistently producing content on a daily basis with no human effort.
Rapid Prototyping: Quickly creating a "good enough" version of an idea to evaluate before investing professional production resources.
Step 5: Leveraging Advanced Research Capabilities
AI Agents can break through information barriers that traditional research tools cannot.
Breaking Through Information Barriers
Navigating Login-Protected Sites: An agent can be given credentials (for a safe, test account) to access platforms like Upwork, academic databases, or private industry forums to gather data.

Gathering Marketplace Data: They can collect real pricing and demand information from freelancer platforms. For example, an agent could be tasked with analyzing the last 100 job posts related to "LangChain" to determine the average hourly rate clients are willing to pay.

Cross-Referencing Multiple Sources: An agent can compile comprehensive reports by gathering information from multiple websites, forums, and social media, then looking for patterns and discrepancies.
Real-World Research Applications
A recent study using AI agents to analyze the AI skills market on freelancer platforms revealed interesting insights:

The majority of AI-related requests were for simple integration tasks (e.g., "connect OpenAI's API to Google Sheets") rather than complex R&D projects.
Deep technical skills like LangChain were less in demand than setting up basic AI workflows for small businesses.
Client needs are often much simpler than what technical communities are discussing online.
This information is extremely valuable for shaping a business strategy or personal career development.
Optimizing The Research Process
Define Research Objectives: Be specific. Instead of
"research the real estate market,"try:"Analyze the average selling price per square meter for 2-bedroom apartments in Thu Duc City, Ho Chi Minh City, based on data from the 50 most recent listings on https://www.google.com/search?q=Batdongsan.com.vn. Categorize by the An Phu, Thao Dien, and Thu Thiem wards."
Identify Target Platforms: List the exact websites, databases, or marketplaces to be investigated.

Set Data Collection Parameters: Specify what information to extract (price, area, number of bedrooms, posting date) and how to organize it (e.g., "export to a CSV file with clearly named columns").

Plan Human Intervention Points: Identify steps where human oversight is needed, such as solving a captcha or making a decision based on complex context.

Establish Verification Methods: Create systems to check the accuracy of the data, such as requiring the agent to cross-check information from two different sources.
Step 6: Automating Presentation And Document Creation
AI Agents can significantly streamline the process of creating presentation decks and documents, saving you hours of work.
Automated Deck Generation
The process typically involves:
Topic Research: You provide a topic, for example,
"The Impact of Quantum Computing on Cybersecurity."The agent will scan reputable sources (like ArXiv, tech journals, expert blogs) to gather information.
Content Synthesis: It will combine text, data, and key points into a coherent slide structure, creating titles, bullet points, and speaker notes.

Visual Enhancement: The agent can search for and incorporate relevant images, charts, and diagrams to illustrate the points being made.

Structure Optimization: It can organize the information in a logical flow, ensuring the presentation has a clear introduction, body, and conclusion.

Quality Assessment And Improvement
While AI-generated presentations may not meet the design standards of a professional graphic artist, they excel at:

Speed: Getting a first draft ready in minutes instead of hours.
Comprehensiveness: Including perspectives or data points you might have missed.
Consistent Formatting: Maintaining consistency in fonts, colors, and layout throughout the presentation.
The most effective approach is to use the AI-generated content as a foundation. You can then spend your time refining the message, adding your own unique insights, and improving the design with specialized tools like Canva or PowerPoint.
Step 7: Understanding Agent Browser Technology
The next evolution of AI automation is agents that run directly within your browser, rather than in a cloud-based virtual machine.
The Future Of Agentic Browsing
Companies like Perplexity are pioneering the development of browsers with the ability to:
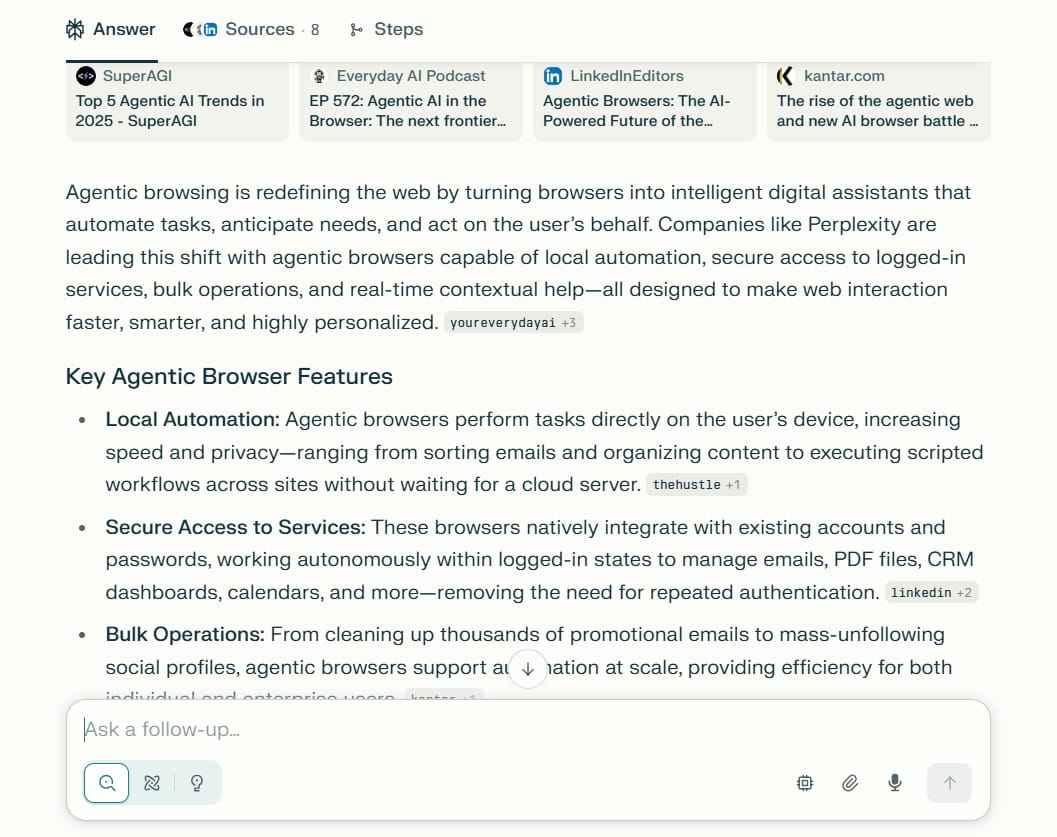
Run Local Automations: Execute tasks without spinning up a remote virtual machine, which increases speed and reduces latency.
Access Logged-In Services: Work securely with your existing accounts and saved passwords, allowing them to manage your email, social media, and other work tools.
Perform Bulk Operations: Handle tasks like cleaning up your inbox (deleting 1000 promotional emails), mass-unfollowing inactive social media accounts, or curating content.
Provide Real-Time Assistance: Offer contextual suggestions and help as you browse the web.
Practical Browser Agent Applications
You could set up automations for daily tasks:
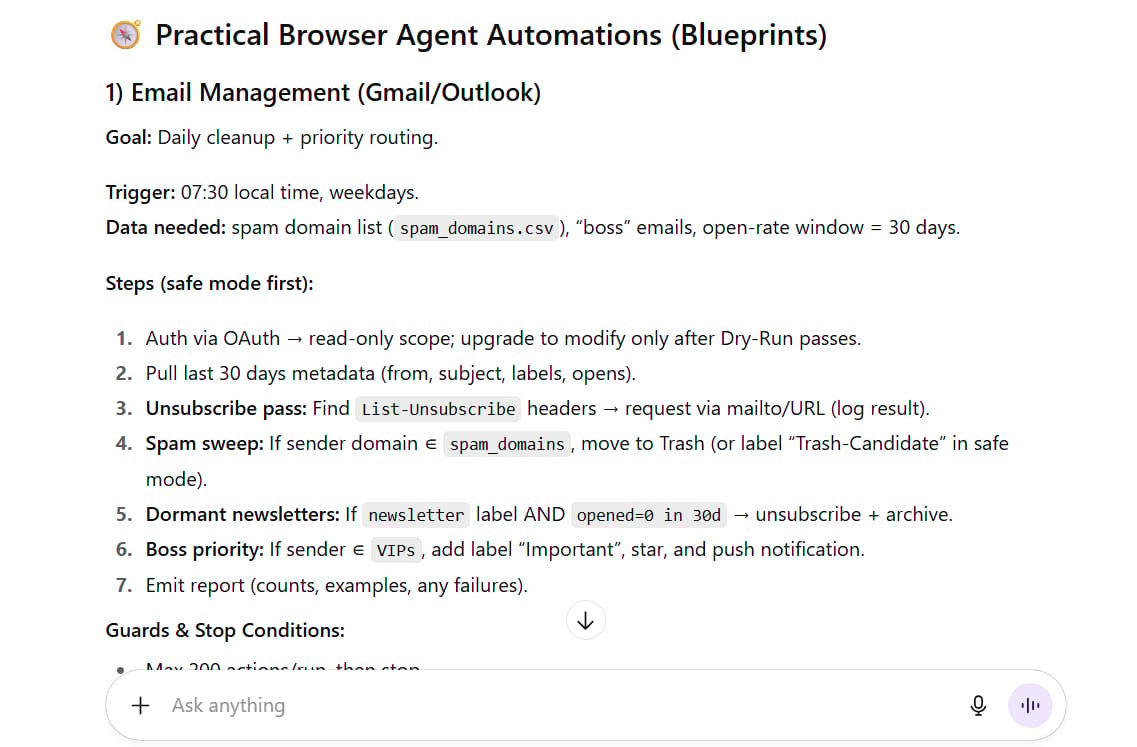
Email Management: "Every day, check my inbox. Delete all emails from domains on my 'spam' list. Unsubscribe me from any newsletter I haven't opened in 30 days. Flag emails from my boss as 'important'."
Content Curation: "Every morning, find the top 5 trending videos on YouTube related to 'sustainable development'. Create a list of the links with a brief summary of each video."
Social Media Management: "Schedule this blog post to be published on both LinkedIn and Twitter tomorrow at 9 AM. Monitor mentions of my brand and flag any negative comments for my review."
The result:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Agent Suite (single file)
- Email Management (Gmail/Outlook-ready stubs)
- Content Curation (YouTube search + summaries stub)
- Social Management (LinkedIn + X/Twitter post + mentions stub)
Features:
- Dry-run vs Apply
- Rate limiting + guards
- Structured logging to JSONL
- CSV/Markdown outputs
- .env configuration
"""
import os, sys, time, csv, json, argparse, random, math, pathlib, datetime as dt
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import List, Dict, Any, Tuple, Optional
# ------------------------------
# Config & Utilities
# ------------------------------
try:
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
except Exception:
pass # optional
ROOT = pathlib.Path(__file__).parent
EXPORTS = ROOT / "exports"
LOGS = ROOT / "logs"
EXPORTS.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
LOGS.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
def now_iso():
return dt.datetime.utcnow().replace(microsecond=0).isoformat()+"Z"
def jitter(seconds=180):
return random.randint(-seconds, seconds)
def rate_sleep(seconds=1.0):
time.sleep(seconds)
def log_jsonl(name: str, record: Dict[str, Any]):
p = LOGS / f"{name}.jsonl"
with p.open("a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(json.dumps({"ts": now_iso(), **record}, ensure_ascii=False) + "\n")
def cap_actions(actions: List[Dict[str, Any]], max_actions: int) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
return actions[:max_actions]
def ensure_env(var: str, optional=False, default=None):
val = os.getenv(var, default)
if not optional and not val:
print(f"[WARN] Missing env: {var}")
return val
# ------------------------------
# Shared Guards
# ------------------------------
@dataclass
class Guards:
max_actions: int = 200
no_delete_under_hours: int = 24
request_per_sec: float = 1.0
neg_alert_threshold: float = 0.7
# ------------------------------
# Email Manager
# ------------------------------
class EmailManager:
def __init__(self, mode: str, guards: Guards):
self.mode = mode # "dry-run" or "apply"
self.guards = guards
self.spam_domains = self._load_domains(EXPORTS / "spam_domains.csv")
self.vips = self._load_vips(EXPORTS / "vips.yml")
def _load_domains(self, path: pathlib.Path) -> set:
if not path.exists(): return set()
with path.open("r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
return set([r.strip().lower() for r in f if r.strip()])
def _load_vips(self, path: pathlib.Path) -> set:
if not path.exists(): return set()
try:
import yaml
data = yaml.safe_load(path.read_text(encoding="utf-8")) or {}
return set(data.get("emails", []))
except Exception:
return set()
def list_messages(self, query: str) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""
TODO: Replace with Gmail/Outlook API calls.
Mocked messages: each has id, from, domain, labels, opened_30d, is_newsletter, date_hours
"""
msgs = []
for i in range(1, 301):
domain = random.choice(["updates.com", "news.io", "vipco.com", "spamville.biz"])
msgs.append({
"id": f"msg_{i}",
"from": f"sender{i}@{domain}",
"domain": domain,
"labels": ["inbox", "newsletter"] if domain in ["updates.com","news.io"] else ["inbox"],
"opened_30d": 0 if random.random() < 0.35 else 1,
"is_newsletter": domain in ["updates.com","news.io"],
"date_hours": random.randint(1, 240), # age in hours
"subject": f"Subject {i}"
})
return msgs
def queue_actions(self, msgs: List[Dict[str, Any]]) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
actions = []
for m in msgs:
# VIP flag
if m["from"] in self.vips or m["domain"] in {"vipco.com"}:
actions.append({"id": m["id"], "action": "label:Important,star", "reason": "vip_sender"})
# Dormant newsletters
if m["is_newsletter"] and m["opened_30d"] == 0 and m["date_hours"] > self.guards.no_delete_under_hours:
actions.append({"id": m["id"], "action": "unsubscribe+archive", "reason": "dormant_newsletter"})
# Spam domains
if m["domain"] in self.spam_domains and m["date_hours"] > self.guards.no_delete_under_hours:
actions.append({"id": m["id"], "action": "trash", "reason": "spam_domain"})
return cap_actions(actions, self.guards.max_actions)
def dry_run_report(self, actions: List[Dict[str, Any]]):
csv_path = EXPORTS / f"email_actions_preview_{dt.date.today().isoformat()}.csv"
with csv_path.open("w", newline="", encoding="utf-8") as f:
w = csv.DictWriter(f, fieldnames=["id","action","reason"])
w.writeheader()
w.writerows(actions)
print(f"[DRY-RUN] Preview written: {csv_path}")
def apply(self, actions: List[Dict[str, Any]]):
# TODO: Implement actual API calls.
for a in actions:
rate_sleep(1.0 / self.guards.request_per_sec)
log_jsonl("email_apply", {"msg_id": a["id"], "action": a["action"], "reason": a["reason"], "status": "OK"})
print(f"[APPLY] Executed {len(actions)} email actions. See logs/email_apply.jsonl")
def run(self):
msgs = self.list_messages(query="newer_than:30d")
actions = self.queue_actions(msgs)
log_jsonl("email_run", {"found": len(msgs), "queued": len(actions), "mode": self.mode})
if self.mode == "dry-run":
self.dry_run_report(actions)
else:
self.apply(actions)
# ------------------------------
# Content Curation (YouTube)
# ------------------------------
class ContentCurator:
def __init__(self, topic: str, mode: str, guards: Guards):
self.topic = topic
self.mode = mode
self.guards = guards
self.keep_top = 5
def search_candidates(self, topic: str) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""
TODO: Replace with YouTube Data API or scrape + transcript API.
Returns list with title, url, channel, published_at (hours_ago), views, likes, short
"""
candidates = []
for i in range(50):
hrs = random.randint(1, 72)
views = random.randint(20_000, 2_000_000)
likes = int(views * random.uniform(0.01, 0.08))
short = random.random() < 0.15
candidates.append({
"title": f"{topic} Explainer #{i+1}",
"url": f"https://youtu.be/mock{i+1}",
"channel": f"Channel{i%12}",
"published_at": (dt.datetime.utcnow()-dt.timedelta(hours=hrs)).isoformat()+"Z",
"views": views,
"likes": likes,
"short": short,
"desc": f"A video about {topic} with data and policies"
})
return candidates
def semantic_relevance(self, text: str) -> float:
# TODO: replace with embeddings. Mock relevance.
return random.uniform(0.6, 0.98)
def recency_score(self, iso_ts: str) -> float:
# Newer = higher score (0..1)
t = dt.datetime.fromisoformat(iso_ts.replace("Z",""))
hours = (dt.datetime.utcnow() - t).total_seconds() / 3600.0
return max(0.0, 1.0 - (hours/72.0))
def views_velocity(self, v: Dict[str, Any]) -> float:
# Simple proxy: views / hours since publish (normalized)
t = dt.datetime.fromisoformat(v["published_at"].replace("Z",""))
hours = max(1.0, (dt.datetime.utcnow()-t).total_seconds()/3600.0)
return min(1.0, (v["views"]/hours)/50000.0)
def likes_ratio(self, v: Dict[str, Any]) -> float:
return min(1.0, (v["likes"]/max(1, v["views"])) / 0.08)
def score(self, v: Dict[str, Any]) -> float:
return (
0.40 * self.views_velocity(v)
+ 0.25 * self.likes_ratio(v)
+ 0.20 * self.recency_score(v["published_at"])
+ 0.15 * self.semantic_relevance(v["title"] + " " + v["desc"])
)
def summarize(self, items: List[Dict[str, Any]]) -> List[str]:
# TODO: replace with LLM call for proper single-sentence summary
out = []
for it in items:
out.append(f"{it['title']} — {it['channel']} — {it['url']} — "
f\"A {self.topic.lower()} update with {it['views']:,} views; published {it['published_at'][:10]}.\")
return out
def run(self):
cands = self.search_candidates(self.topic)
# Guards
cands = [c for c in cands if not (c["short"] and "explainer" not in c["title"].lower())]
scores = []
for c in cands:
s = self.score(c)
scores.append((s, c))
rate_sleep(1.0 / self.guards.request_per_sec)
top = [c for s,c in sorted(scores, key=lambda x: x[0], reverse=True)[:self.keep_top]]
# Outputs
md_path = EXPORTS / f"curation_{self.topic.replace(' ','_').lower()}_{dt.date.today().isoformat()}.md"
csv_path = EXPORTS / f"curation_{self.topic.replace(' ','_').lower()}_{dt.date.today().isoformat()}.csv"
summaries = self.summarize(top)
with md_path.open("w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
for i, (item, summ) in enumerate(zip(top, summaries), 1):
f.write(f"- {i}) **{item['title']}** — {item['channel']} — {item['url']} \n")
f.write(f" {summ}\n")
with csv_path.open("w", newline="", encoding="utf-8") as f:
w = csv.DictWriter(f, fieldnames=["rank","title","url","channel","published_at","views","likes","score"])
w.writeheader()
for rank, item in enumerate(top, 1):
w.writerow({
"rank": rank, "title": item["title"], "url": item["url"], "channel": item["channel"],
"published_at": item["published_at"], "views": item["views"], "likes": item["likes"],
"score": round(self.score(item), 4)
})
log_jsonl("curation_run", {"topic": self.topic, "candidates": len(cands), "selected": len(top), "mode": self.mode,
"outputs": [str(md_path), str(csv_path)]})
print(f"[OK] Curation saved: {md_path}\n[OK] CSV: {csv_path}")
# ------------------------------
# Social Manager
# ------------------------------
class SocialManager:
def __init__(self, mode: str, guards: Guards):
self.mode = mode
self.guards = guards
self.sensitive_topics = {"politics", "religion"} # extend with sensitive_topics.yml if needed
# --- Posting ---
def schedule_post(self, network: str, text: str, when_iso: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
TODO: Replace with LinkedIn + X/Twitter APIs or scheduler.
"""
if len(text) > (280 if network == "twitter" else 3000):
text = text[:277] + "..."
if any(s in text.lower() for s in self.sensitive_topics):
return {"ok": False, "reason": "sensitive_topic_blocked"}
if self.mode == "dry-run":
return {"ok": True, "scheduled": when_iso, "post_id": f"{network}_DRY_{random.randint(1000,9999)}"}
# APPLY mode stub:
rate_sleep(1.0 / self.guards.request_per_sec)
return {"ok": True, "scheduled": when_iso, "post_id": f"{network}_{random.randint(10000,99999)}"}
# --- Mentions monitoring ---
def fetch_mentions(self, network: str, brand: str, since_id: Optional[str]) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""
TODO: Replace with API search.
"""
sample = []
for i in range(random.randint(2,8)):
text = random.choice([
f"I love {brand}, great docs!",
f"{brand} support is slow today.",
f"Trying {brand} with my team—first impressions good."
])
sample.append({"id": f"{network}_{i}", "url": f"https://{network}.com/post/{i}", "text": text})
return sample
def sentiment(self, text: str) -> Tuple[str, float]:
# Very naive mock; replace with model/LLM
tl = text.lower()
if "slow" in tl or "bad" in tl or "hate" in tl:
return "neg", 0.8
if "love" in tl or "great" in tl or "good" in tl:
return "pos", 0.8
return "neu", 0.55
def suggest_reply(self, text: str) -> str:
return ("Thanks for flagging this—totally fair point about the issue. "
"We’re looking into it now and will update shortly. "
"Feel free to DM details so we can make it right.")
def monitor(self, brand: str, networks: List[str], since_id: Optional[str]=None):
alerts = []
for net in networks:
items = self.fetch_mentions(net, brand, since_id)
for it in items:
s, conf = self.sentiment(it["text"])
rec = {"network": net, "id": it["id"], "url": it["url"], "sentiment": s, "conf": conf, "text": it["text"]}
if s == "neg" and conf >= self.guards.neg_alert_threshold:
rec["suggested_reply"] = self.suggest_reply(it["text"])
alerts.append(rec)
log_jsonl("social_mentions", rec)
return alerts
# ------------------------------
# CLI
# ------------------------------
def build_parser():
p = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Agent Suite (single-file)")
p.add_argument("--mode", choices=["dry-run","apply"], default="dry-run", help="Execution mode")
sub = p.add_subparsers(dest="cmd", required=True)
pe = sub.add_parser("run-email", help="Run Email Manager")
pe.add_argument("--max-actions", type=int, default=200)
pc = sub.add_parser("run-curation", help="Run Content Curation")
pc.add_argument("--topic", type=str, default="sustainable development")
ps = sub.add_parser("run-social", help="Run Social Manager")
ps.add_argument("--post", type=str, help="Text to schedule (if provided)")
ps.add_argument("--when", type=str, help="ISO time for scheduling (e.g., 2025-09-09T09:00:00Z)")
ps.add_argument("--brand", type=str, default="YourBrand")
ps.add_argument("--monitor", action="store_true", help="Monitor mentions (hourly loop disabled; one-shot)")
pall = sub.add_parser("run-all", help="Run all agents (one-shot)")
pall.add_argument("--topic", type=str, default="sustainable development")
pall.add_argument("--brand", type=str, default="YourBrand")
pall.add_argument("--max-actions", type=int, default=200)
return p
def main():
args = build_parser().parse_args()
guards = Guards(max_actions=getattr(args, "max_actions", 200))
if args.cmd == "run-email":
EmailManager(args.mode, guards).run()
elif args.cmd == "run-curation":
ContentCurator(args.topic, args.mode, guards).run()
elif args.cmd == "run-social":
sm = SocialManager(args.mode, guards)
if args.post and args.when:
res_tw = sm.schedule_post("twitter", args.post, args.when)
res_li = sm.schedule_post("linkedin", args.post, args.when)
print("[SCHEDULED]", res_tw)
print("[SCHEDULED]", res_li)
log_jsonl("social_schedule", {"twitter": res_tw, "linkedin": res_li})
if args.monitor:
alerts = sm.monitor(args.brand, ["twitter","linkedin"], since_id=None)
if alerts:
print("[ALERTS]")
print(json.dumps(alerts, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False))
else:
print("[OK] No negative mentions above threshold.")
elif args.cmd == "run-all":
EmailManager(args.mode, guards).run()
ContentCurator(args.topic, args.mode, guards).run()
sm = SocialManager(args.mode, guards)
alerts = sm.monitor(args.brand, ["twitter","linkedin"], since_id=None)
if alerts:
print("[ALERTS]", json.dumps(alerts, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()Step 8: Managing Risks And Understanding Limitations
As AI Agents gain more powerful capabilities, risk management becomes critically important.
Financial And Security Considerations

Payment Controls: Never give an agent unrestricted access to financial accounts. Always be the final approver for any transaction.
Investment Decisions: Avoid letting agents make investment choices. They can analyze data, but they lack human context and risk tolerance.
Data Security: Be cautious about which platforms you allow agents to access if they contain sensitive information.
Account Separation: Use dedicated email, social media, and financial accounts specifically for agent testing to limit potential damage.
Prompt Engineering Best Practices
Effective control of AI Agents requires precision:
Be Extremely Specific: Vague instructions lead to unpredictable results.
Set Clear Boundaries: Always include stopping conditions, quantity limits, and constraints.
Use Examples and References: Provide concrete examples of the desired outcome. "Here is an example of a good outreach message: [insert example]."
Test with Low-Stakes Tasks: Practice with reversible actions (like research, content creation) before moving to high-impact automation (like client outreach, purchasing).
Monitor Continuously: Especially in the early stages, watch the agent's behavior and be ready to intervene.
Technical Limitations To Understand
Current AI Agents still have limitations:
Cannot Use Desktop Software: They are confined to browser-based applications. They cannot open Photoshop or Excel on your local machine.
Handle Complex Creative Tasks: Output quality for video and design is still basic.
Make Nuanced Decisions: They struggle with tasks that require human judgment, empathy, or cultural understanding.
Maintain Long-Term Context: In very long and complex workflows, they can "forget" the original objectives.
Step 9: Building Your Own Agent Workflow System
The real power is unlocked when you start combining agent capabilities into a personal or business automation system.
Setting Up Daily Automation

Identify Tasks: List the repetitive tasks you perform daily or weekly. (e.g., checking competitor pricing, creating social media reports, filtering emails).
Assess Automation Potential: Determine which tasks are suitable for an agent (browser-based, rule-driven).
Design the Workflow: Write out the step-by-step process you want the agent to follow in the form of a detailed prompt.
Test and Refine: Start with simple tasks and gradually increase complexity. Each test is an opportunity to improve your prompt.
Monitor Performance: Track success rates and identify opportunities for improvement.
Applications For Agencies And Businesses
For businesses, AI Agents enable:

Scalable Service Delivery: Handle more clients without a proportional increase in staff. For example, an SEO agency could use an agent to generate monthly technical reports for 100 clients simultaneously.
Outcome-Based Pricing: Instead of billing by the hour, agencies can focus on delivering results, as much of the execution work is automated.
Rapid Prototyping: Quickly test new service ideas before a full-scale rollout.
Quality Control: Ensure a consistent standard of output for tasks like keyword research or competitor analysis, regardless of which team member performs them.
Step 10: Preparing For The Agent-Driven Future
The agent revolution will profoundly reshape the job market and business models.
Industry Transformation Predictions

New Job Categories: There will be a high demand for roles like "Agent Supervisor," "Senior Prompt Engineer," and "Workflow Automation Specialist."
Changed Business Models: The shift from selling software licenses to selling outcome-based services will accelerate.
Enhanced Personal Branding: Individual expertise becomes more discoverable and valuable. Agents will be able to find "the best person" for a specific task.
Accelerated Business Growth: Companies can scale faster with automated assistance, reducing barriers related to personnel and costs.
Skills For The Agent Era
To thrive in an agent-driven world, focus on these non-automatable skills:

Domain Expertise: Deep knowledge in a specific field is more valuable than ever. The AI can execute, but it needs a human expert to provide direction.
Semantic Precision: The ability to articulate complex requirements and objectives into precise, unambiguous instructions for an AI.
Strategic Thinking: Understanding what should be automated versus what requires a human touch. This is the art of human-agent teaming.
Adaptability: A willingness to experiment with new tools and approaches. This technology is evolving weekly, not yearly.
Risk Assessment: The ability to evaluate when agent automation is appropriate and when it poses too much risk.
Get Started Today
The key to mastering AI Agents is to start experimenting immediately. Begin with low-risk tasks like research and content creation, then gradually expand to more complex automations. Remember that we are still in the early stages of this technology - what seems impossible today may be routine in six months.
Don't be skeptical about AI's capabilities. The technology consistently exceeds expectations. Instead of doubting what's possible, focus on identifying where agents can add value to your work and personal life.
The future belongs to those who can clearly articulate what they want and effectively direct AI Agents to achieve those goals. Start building your agent skills today, and you will be ahead of the curve as this technology becomes mainstream in the coming months and years.
The era of AI Agents isn't coming - it's already here. The question isn't whether you should learn to use them, but how quickly you can master them to stay competitive in an increasingly automated world.
Ready to start your AI agent journey? Begin with simple tasks, be specific with your instructions, and always prioritize safety and ethical considerations. The future of work is being written right now, and AI Agents are holding the pen.
If you are interested in other topics and how AI is transforming different aspects of our lives or even in making money using AI with more detailed, step-by-step guidance, you can find our other articles here:
How useful was this AI tool article for you? 💻Let us know how this article on AI tools helped with your work or learning. Your feedback helps us improve! |
Reply