- AI Fire
- Posts
- 💥 China's Kimi K2: The AI Model That Changes The Game For The US
💥 China's Kimi K2: The AI Model That Changes The Game For The US
Is China winning the AI race? Kimi K2, a new model with revolutionary tech, suggests yes. We analyze how China is now challenging US dominance.

Before reading this analysis, who do you believe is currently LEADING the global AI race? |
Table of Contents
For over a year, the global artificial intelligence (AI) race has seemed like a one-man show starring America's tech giants. OpenAI with its GPT series, Google with Gemini, and Anthropic with Claude have continuously made massive waves, shaping public opinion and attracting billions in investment. Against this backdrop, efforts from China were often downplayed, dismissed as clumsy copies or merely attempts to catch up. But the arrival of Kimi K2 from the Moonshot AI lab is more than just a warning. It is a powerful statement, definitive proof that the landscape has shifted.

The earlier appearance of DeepSeek was the first signal, but with Kimi K2, no one can afford to look away now. This model has not only caught up, but in many respects, it is leading the way and charting a new path. This article will provide a deep analysis of the technical breakthroughs behind Kimi K2, explore how it redefines the core principles of AI training, and more importantly. This is no longer a story about who will win the AI race; it is a story about whether the West is losing a race it started itself.
Part 1: Kimi K2 - Shattering All Performance Norms
To understand the stature of Kimi K2, we must first look at its numbers and real-world performance. This is not a "theoretical" model but a powerful, efficient, and proven machine.
1.1. A Massive Architecture With Superior Speed

Kimi K2 is a large language model (LLM) built on a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture. In theory, it possesses one trillion parameters, a colossal figure that places it in the same weight class as the world's largest models. However, the core principle of the MoE architecture is that at each prediction step, only a small fraction of the "experts" are activated. For Kimi K2, only 32 billion active parameters are used for each generated token, which is about 3.2% of the total.
The MoE mechanism can be visualized as a council of top experts in various fields. When a question is received, instead of everyone answering at once, the system assigns the most suitable few experts to solve that problem. This allows the model to possess vast knowledge (corresponding to the huge total parameter count) while maintaining high processing speed and computational efficiency (by activating only a small fraction of parameters).
Moonshot AI has released two versions to the community:
Kimi-K2-Base: The foundational version, ideal for researchers and other labs to fine-tune and build their own variants.

Kimi-K2-Instruct: A version fine-tuned to follow instructions and optimized for "agentic" chat experiences. This is a more ready-to-use model.

1.2. Dominating The Benchmarks
Kimi K2 not only impresses with its architecture but also demonstrates superior strength across a range of standard benchmarks, particularly in the following areas:
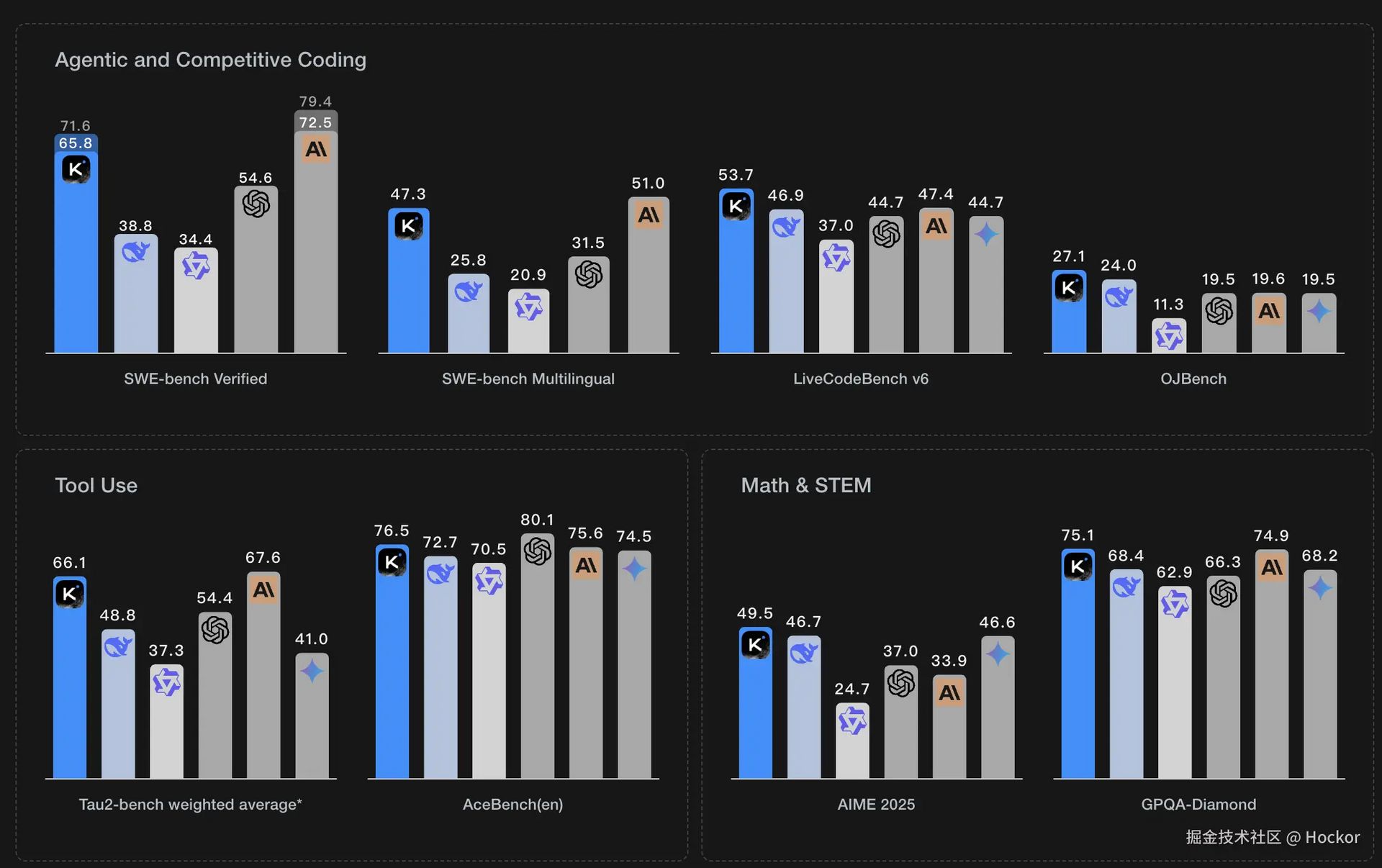
Coding: It is recognized as the best open-source model for programming capabilities, even rivaling top proprietary models in many tests.
Tool Use: This is one of its brightest spots. The ability to integrate and use external tools (APIs, calculators, search engines) is key for agentic AI tasks, and Kimi K2 has proven its superiority in this domain.
In-depth Knowledge: The model exhibits deep understanding across many fields, especially in the natural sciences.
Emotional Intelligence (EQ): In an EQ benchmark, Kimi K2 achieved the highest score, surpassing all other advanced models. This demonstrates its ability to understand and respond to human emotional nuances, a critical factor for creating natural interactions.
However, it's important to clarify that Kimi K2 is classified as a "non-reasoning model." It is not directly compared to models designed for "deep thought" like GPT-4o3 or Gemini 2.5 Pro. The reason is that Kimi K2 does not generate complex chains of thought to answer questions. But as we will see, this does not mean it isn't a "deep thinker" in a very different way.
Learn How to Make AI Work For You!
Transform your AI skills with the AI Fire Academy Premium Plan - FREE for 14 days! Gain instant access to 500+ AI workflows, advanced tutorials, exclusive case studies and unbeatable discounts. No risks, cancel anytime.
Part 2: Innovation From The Roots: The Technical Secrets Behind Kimi K2
What makes Kimi K2 truly special isn't just its performance, but how it challenges some of the most established foundations of modern AI.
2.1. Rethinking Scaling Laws: The "Agentic" Approach
In AI, progress has been primarily driven by two scaling laws:
Pretraining scaling law: The widely-verified notion that to increase a model's "intelligence," we must increase the size of the training dataset and the model size accordingly. Bigger models are better models.
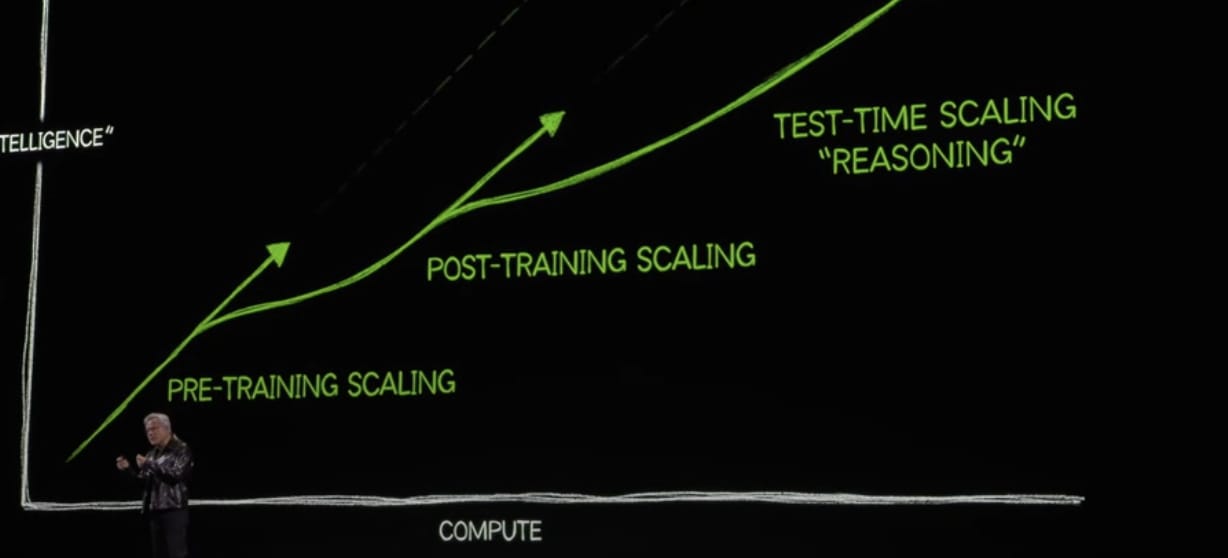
Test-time training scaling law: As the first law began to show diminishing returns, the focus shifted to increasing the amount of computation a model allocates to solving a problem at runtime. Models that "think" longer on a task produce better results.
Models following the second law are often called "reasoning models." The common method to create them is:
Train a base model: Use internet-scale data to teach the model to mimic text.
Fine-tune with Chain-of-Thought (CoT): Teach the model to imitate reasoning traces (problem → step-by-step reasoning → solution) on a smaller dataset. This helps the model learn to break down complex problems, especially in verifiable domains like math and programming.

Reinforcement Learning: Let the model find its own path to the solution instead of imitating one. The model is "rewarded" for correct solutions. This "trial-and-error" process is extremely effective in verifiable domains because we know for sure if an answer is right or wrong.
The limitation of this method is that it creates "geniuses" in math and code but doesn't lead to significant progress in non-verifiable domains like artistic creation, literary analysis, or complex strategic planning.
And this is where Kimi K2 makes its move.
Instead of forcing the model to "think longer" with difficult math problems, Moonshot AI chose a completely new path: training the model in agentic settings that simulate the real world.
They created a massive dataset of thousands of complex scenarios that require the model to use tools like search engines, calculators, and booking APIs to complete tasks. Instead of abstract examples, imagine the specific tasks Kimi K2 was trained to solve:
Example 1 (Travel Planning): "Plan a 3-day, 2-night trip to Da Nang for a couple in September. Requirements: find round-trip Vietjet Air tickets for under 2 million VND per person, book a 4-star hotel with a sea view on Agoda, and suggest a detailed itinerary including Ba Na Hills, eating seafood at My Khe beach, and visiting Hoi An ancient town in the evening."
Example 2 (Work Management): "Analyze the attached Q2 revenue report file, summarize the key points into a 5-slide PowerPoint presentation, then draft an email to the management board with the subject 'Summary Report - Q2 2025 Revenue' and attach the PowerPoint file."
By using Reinforcement Learning on this dataset, Kimi K2 learns to solve problems through self-reflection and experimentation. It is rewarded not only for completing the task (booking the ticket, creating the file) but also for the efficiency and logic of its process.
The result? A model with an average token sequence length three times longer than typical "non-reasoning" models. It naturally tends to "think deeper" not because it's forced to solve math problems, but because real-world problems inherently demand that complexity. This approach creates a model born to act, to be a true "agent" in the digital world.
2.2. Challenging "The Bitter Lesson": Optimizing With Muon
For years, the AI industry has been dominated by a philosophy known as "The Bitter Lesson" by Richard Sutton: methods that leverage raw computational power will ultimately win. In other words, "all you need is compute and data."

But Chinese labs, constrained by US sanctions limiting their access to the most advanced GPUs, cannot play this game. They were forced to innovate. Necessity became the mother of invention, and their innovation struck at one of the most fundamental components of AI training: the optimization algorithm.
To understand this, let's review the basic training process of a neural network:
Forward Pass: The model makes a prediction.
Calculate Error: The prediction is compared to the correct result to calculate the "error."
Backward Pass: The backpropagation algorithm is used to calculate the influence (gradient) of each parameter on the error.
Update Parameters: An optimizer is used to update the parameters to minimize the error over time.
For over a decade, AdamW (an improved version of Adam, published in 2017) was the undisputed king of optimizers. Virtually every leading LLM was trained with it.
Kimi K2 is the first large-scale model in the world to abandon AdamW and use a new algorithm called Muon. This algorithm, proposed in a late-2024 blog post by Keller Jordan, aims to update parameters more efficiently by updating them in blocks rather than individually.
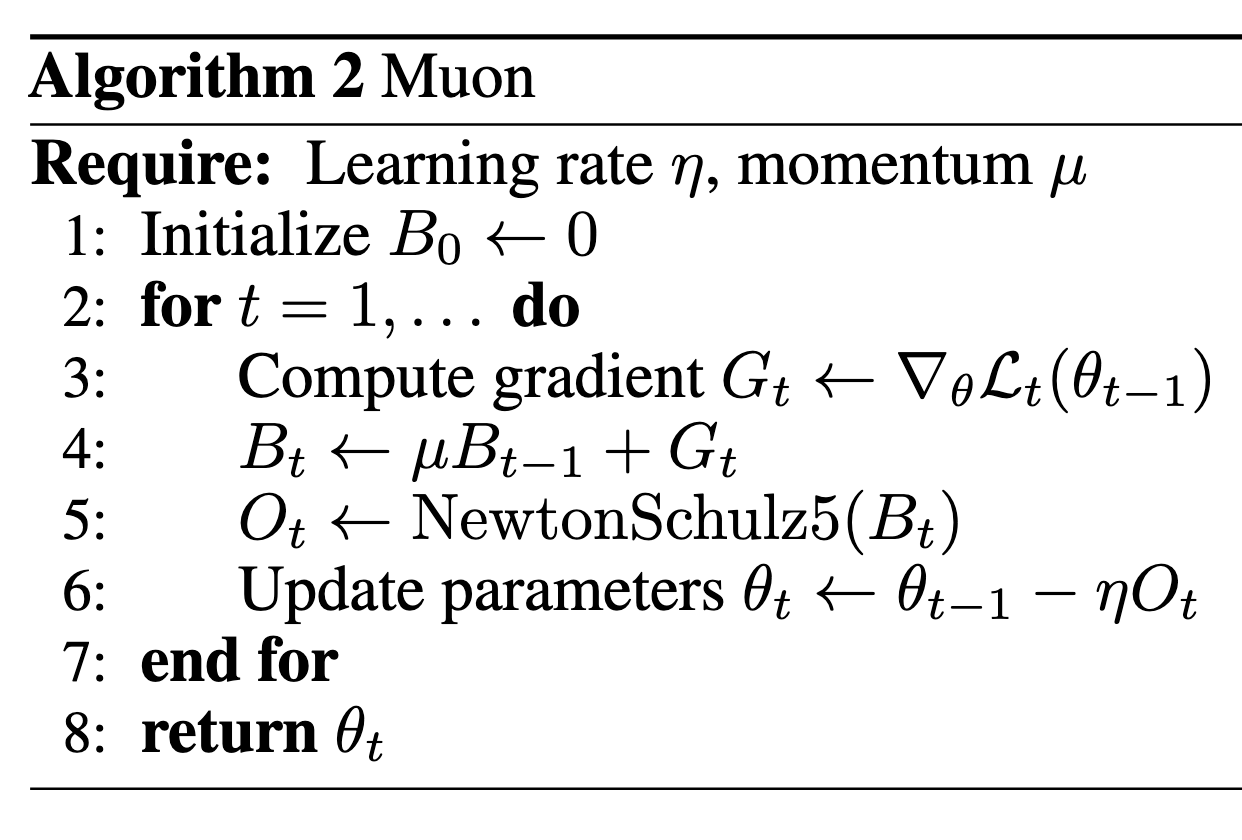
Technical Intuition: AdamW only uses the first derivative (gradient) to find the steepest downhill direction. Muon adds information from the second derivative to calculate the "curvature" of the loss surface. This helps it choose a path that is not only steep but also "smooth," leading to faster and more stable convergence.
The proof is in the pudding: Kimi K2's loss curve during training is remarkably stable, a rarity for a trillion-parameter model.
Why is this change so important?
The answer is token efficiency. Kimi K2 learns more from the same amount of data. It converges faster, which means it saves a massive amount of computational resources and data. The model was trained with only 15 trillion tokens, a fraction of the data used for Western models of similar scale.
This sends a powerful message: maybe we aren't running out of training data as Elon Musk fears. Maybe the problem is that current models are incredibly "wasteful" with data. Kimi K2 proves that by innovating at the algorithmic level, we can achieve comparable or better performance with fewer resources. This is unbelievable news for an industry that has long considered data and compute to be everything.
2.3. A Deeper Technical Dive: MoE Vs. Traditional Architectures
Kimi K2's choice of the MoE architecture is a strategic masterstroke, born from the necessity of compute constraints. To appreciate this, one must compare it to the traditional "dense" Transformer architecture that powers models like GPT-3.
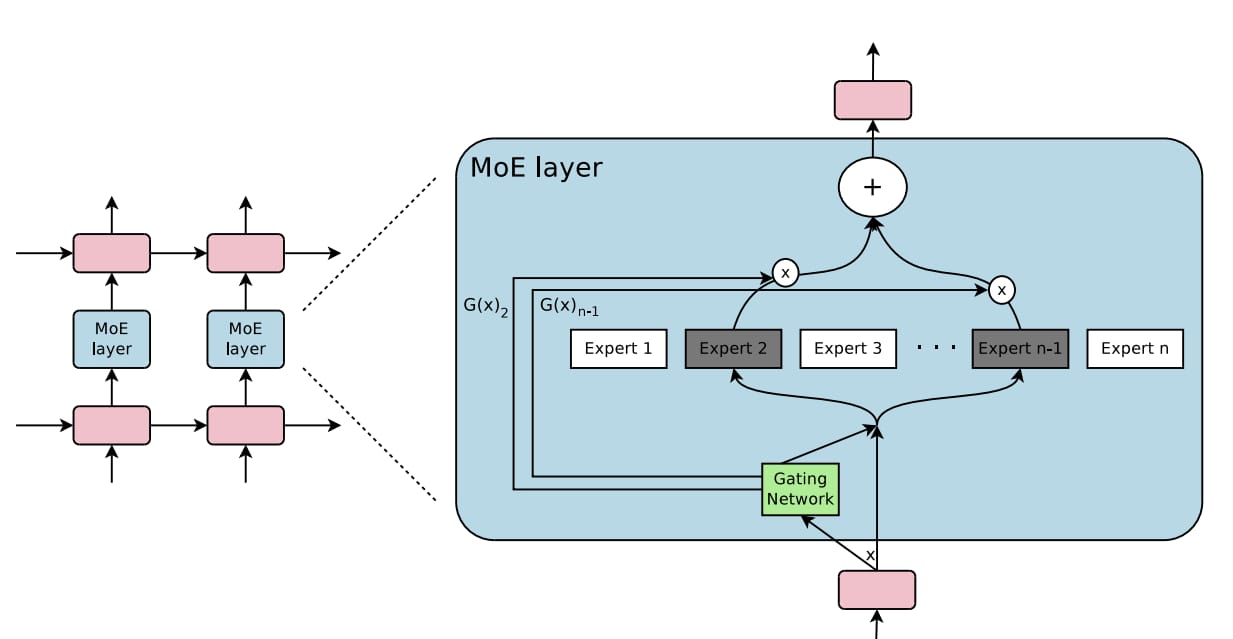
In a dense Transformer, every single parameter is activated for every single token that is processed. Imagine a library where, to answer a single question, the librarian must read every single book on every shelf. It is incredibly thorough but astronomically expensive in terms of computational energy. This is why scaling dense models becomes exponentially more difficult and costly.
The Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture, in contrast, is like a library with highly specialized librarians for every section (history, physics, art, etc.). When a question arrives, a routing network quickly determines which one or two librarians are best suited to answer it. Only those experts are "activated" to process the request. This sparse activation means MoE models can have an enormous number of parameters (experts) in total, granting them vast knowledge, while keeping the actual computational cost for any given task relatively low.
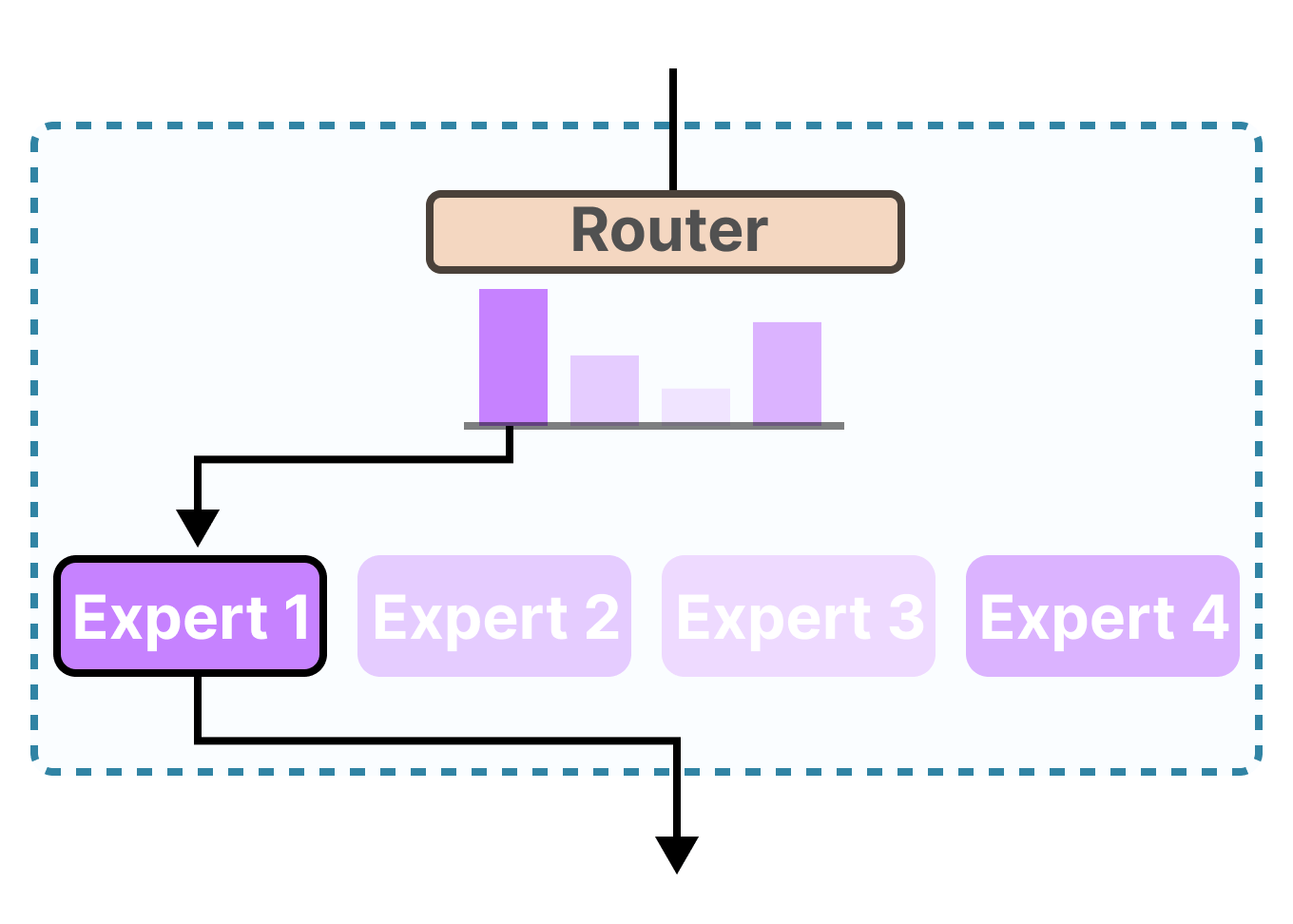
The primary challenge of MoE is managing the complexity. The routing network must be intelligent, and there is communication overhead between the experts. However, when executed correctly, as Kimi K2 demonstrates, MoE provides a path to scale model knowledge far more efficiently than the brute-force approach of dense models, offering a perfect solution for those who cannot rely on infinite compute.
Part 3: Geopolitical Significance - When the Game Changes
Kimi K2's technical breakthroughs are not just academic curiosities. They are geopolitical shockwaves, signaling a tectonic shift in the global AI race.
3.1. Open Source - The New Geopolitical Weapon
Moonshot AI's decision to open-source Kimi K2 was not a random act. It was a strategic move. While US labs are increasingly closing off their most advanced models to protect their commercial advantage, China is using open source as a weapon.

By providing a world-class model for free, they achieve multiple goals simultaneously:
Neutralizing the Compute Advantage: US GPU sanctions become less effective when the global community can access, fine-tune, and improve a top-tier model without needing the infrastructure of American corporations.
Steering Global Research in Their Direction: Researchers worldwide will build upon Kimi K2's foundation, creating an ecosystem dependent on Chinese core technology.
Winning "Goodwill": They are perceived as promoters of humanity's collective progress, while Western companies are seen as focused solely on profit.
Exerting Economic Pressure: US companies trying to sell proprietary models will face fierce competition from free, equally powerful open-source alternatives.
3.2. China's Synergy Vs. America's Fragmentation
A notable point is the collaboration and mutual advancement among Chinese labs. Kimi K2 is said to have a nearly identical architecture to DeepSeek v3, with only minor differences. This indicates an ecosystem fighting together as a team, treating the AI race as a matter of national interest.

Meanwhile, in Silicon Valley, we see a completely different picture:
The Talent War: Companies are willing to pay hundred-million-dollar compensation packages to "poach" key researchers from each other.
Petty Disputes: Public lawsuits like the one between Elon Musk and Sam Altman weaken the industry's image and focus.
Arbitrary Regulation: Lobbying efforts for regulations like SB 1047 in California could stifle startups and entrench the monopolies of the current giants.
All of this creates an unavoidable feeling: while Chinese labs are fighting for a national goal, American labs are fighting for their investors' profits.
3.3. Beyond Moonshot: China's National AI Ecosystem

Kimi K2 did not emerge from a vacuum. It is the brilliant tip of a massive, state-coordinated iceberg. To view Moonshot AI as an isolated success is to miss the larger picture of China's national AI strategy. Other tech giants are formidable players in their own right: Baidu's Ernie Bot is deeply integrated into its search and cloud empire; Alibaba's Tongyi Qianwen powers its e-commerce and enterprise solutions; and Tencent's Hunyuan model leverages its dominance in social media and gaming.
What truly binds these efforts is the overarching hand of the state. China's "New Generation Artificial Intelligence Development Plan" is not mere rhetoric. It is a comprehensive national strategy that mobilizes state funding, sets clear technological priorities, and fosters deep collaboration between private companies, state-owned enterprises, and top universities. This creates a synergistic ecosystem where breakthroughs in one lab (like DeepSeek) are quickly learned, adapted, and built upon by others (like Moonshot). This concerted, nationalistic push stands in stark contrast to the more fragmented, market-driven, and often adversarial environment of Silicon Valley.
3.4. The Economic Ripple Effect: Open Source As A Market Disruptor
The proliferation of powerful, free, open-source models like Kimi K2 is poised to trigger significant economic and social disruption. The most immediate impact is on the business models of companies like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google, whose revenue relies heavily on selling API access to their proprietary models. Why pay per token when a comparable, or in some cases superior, model can be run locally for a fraction of the cost?

This "democratization" of AI empowers smaller businesses, startups, and research institutions worldwide. They can now build sophisticated AI applications without being beholden to the pricing and terms of a few American tech giants. For developing nations, this could unlock unprecedented opportunities for innovation.
However, this disruption also carries social risks. The widespread availability of uncensored, powerful models makes it easier for bad actors to generate misinformation, create malicious code, or engage in other harmful activities. While closed models can enforce safety guardrails, open-source models place the onus of responsible deployment on the end-user, creating a new and complex challenge for global governance.
3.5. The American Counter-Play: What Can the US Do?
Faced with this new reality, the United States is not without options, but it will require a strategic shift. The potential counter-plays fall into several categories:
Policy and Regulation: Washington could escalate its export controls beyond just hardware, potentially targeting AI software, talent, or methodologies. Simultaneously, it could dramatically increase federal funding for domestic AI research through initiatives like the National AI Initiative, aiming to out-innovate the competition.

Corporate Strategy: American tech firms may double down on the "closed" model, emphasizing safety, reliability, and seamless integration as their key value propositions. Forming even stronger, more exclusive alliances (like the Microsoft-OpenAI partnership) to create technological "moats" is another likely path.

Fostering an Open-Source Counterweight: The US could choose to fight fire with fire. By championing its own open-source titans, such as Meta with its Llama series or the multi-company AI Alliance, it can compete directly with China for the hearts and minds of the global developer community, ensuring the open-source ecosystem does not become a Chinese monopoly.
3.6. A Lesson From History: National Interest Must Precede Profit
There is an irony here. A significant portion of America's current economic and technological power was built on foundations that were initially treated as matters of national security and interest, where profit was a secondary concern. The Internet (an effort of the Department of Defense's ARPANET) and GPS (a military system) are two prime examples. They were created for strategic purposes, and only later did American corporations reap trillions by building commercial applications on top of them.

When America realized a technology was a matter of national survival, profit took a backseat. Right now, it is clear which superpower is applying this philosophy to the letter in the AI race, and the sad answer is not the United States.
The claims from American tech CEOs that they "don't really care about the money" and just want to "build AGI" and advance humanity sound hollow when their actions suggest the opposite.
Conclusion: What Future For The AI Race?
Kimi K2 is not just a large language model. It is a shock to the system, a product of the combination of radical innovative thinking and circumstantial pressure. It proves that a lack of resources can be the most powerful driver of creativity.
The message from China is loud and clear: "We have not only caught up; we are pushing the frontier forward." They are reshaping the rules of the game, turning their weaknesses into strengths and exploiting the cracks in the West's strategy.
The elephant in the room is no longer an elephant; it has become a Diplodocus that no one can pretend not to see. The West, particularly the US, can continue to look away, but the reality is that the global open-source ecosystem is increasingly being shaped and led by models from China.
If America's current approach - with its focus on short-term profits, internal feuds, and the lack of a unified national strategic vision - is how it intends to win the AI race, then perhaps it is time to bet on the other side. The playing field has been leveled, and perhaps, it is beginning to tilt in a direction no one expected.
If you are interested in other topics and how AI is transforming different aspects of our lives or even in making money using AI with more detailed, step-by-step guidance, you can find our other articles here:
How useful was this AI tool article for you? 💻Let us know how this article on AI tools helped with your work or learning. Your feedback helps us improve! |
Reply