- AI Fire
- Posts
- 🛠️ How To Master AI Automation Fast: The 10 Essential n8n Nodes (Part 1)
🛠️ How To Master AI Automation Fast: The 10 Essential n8n Nodes (Part 1)
Stop trying to learn every tool. This beginner's guide shows the 10 core n8n nodes (like HTTP Request and Switch) that power 80% of all AI automations

TL;DR BOX
Many users are overwhelmed by n8n’s vast library but mastering just 10 foundational nodes covers 80% of automation needs. Part 1 of this guide focuses on essential triggers, data handling, logic and flow control.
Core nodes include "Schedule" and "Event" triggers to start workflows, "Google Sheets" for database management and "Edit Fields" to clean data. Logic nodes like "IF" and "Switch" direct paths, while "HTTP Request" connects to any API. Flow management relies on "Sub-Workflows", "Loop Over Items" and "Split Out" to handle complex data structures efficiently.
Key points
Stat: The "Loop Over Items" node is critical for preventing API rate limit crashes by processing lists (e.g., 100 emails) one at a time.
Mistake: Sending a raw list to a Gmail node often errors; use the "Split Out" node first to separate the list into individual items.
Action: Use "Sub-Workflows" to build reusable tools (like a dedicated research agent) that can be plugged into multiple different automations.
Critical insight
The HTTP Request node is the "universal translator" that future-proofs your skills, allowing you to connect n8n to any new software immediately, even if a dedicated integration node doesn't exist yet.
🤯 What’s your biggest frustration with automation right now? |
Table of Contents
I. Introduction: Don't Learn Everything, Learn What Matters
Learning n8n can feel like walking into a giant hardware store with no labels. There are tools everywhere. Everything looks useful. And you have no idea what to pick up first.
After building more than 200 AI automations for clients, tutorials and my own business, I noticed something surprising.
I only use a handful of nodes.
You don't need to learn the entire toolbox. You just need to master the essentials. So in this two-part series, I'll walk you through the 17 nodes that power 80% of real AI automation workflows.
In Part 1, we'll start with the first 10 core nodes. These are simple, powerful and form the foundation for almost every AI automation you'll ever build.
Let’s take the first step.
II. What Are The Core Nodes For Getting Data In And Out?
Answer
The first layer is about how workflows start and where data lives. Schedule Trigger acts like an alarm clock that runs workflows on a time schedule. Event triggers like Gmail, Slack, or Form Trigger act like doorbells that fire when something happens. Google Sheets works as a simple database you can see and edit. Edit Fields (Set) cleans, renames, creates, and removes data fields so other nodes do not break.
Key takeaways
Schedule Trigger = proactive automation on a schedule.
Event triggers = reactive automation when something happens.
Google Sheets = easy, visual database for reading and writing data.
Edit Fields = normalizes and labels data so every node understands it.
Critical insight
If data does not enter cleanly or stay organized, no “smart” automation will save you. Inputs and structure decide how far you can go.
1. Schedule Trigger, The "Alarm Clock"
This is the simplest node but it is necessary for proactive AI automation.
What It Does: Think of this like the alarm clock on your phone. You tell it when to wake up and it wakes up your workflow. You can set it to run every morning at 8:00 AM, every Monday or every hour.
Why It Matters: You use this for proactive work. You don't wait for an email to come in. You want the robot to do work for you while you sleep.
Example: Every morning at 6 AM, wake up, check the news and send me a summary.

2. Event Triggers, The "Doorbell"
If the Schedule Trigger is an alarm clock, this is the doorbell.
What It Does: It sits there and waits silently. It only does something when an event happens outside.
Why It Matters: This makes your AI automation reactive. You can't sit at your computer refreshing your email all day. This node does it for you. As soon as the "doorbell" rings, the workflow starts.

Learn How to Make AI Work For You!
Transform your AI skills with the AI Fire Academy Premium Plan - FREE for 14 days! Gain instant access to 500+ AI workflows, advanced tutorials, exclusive case studies and unbeatable discounts. No risks, cancel anytime.
3. Google Sheets, The "Digital Notebook"
This is the most useful free tool you have for managing data in any AI automation.
What It Does: It lets your automation read from or write to a spreadsheet.
Read: The robot looks at a list of leads you put in a sheet.
Write: The robot finds a new lead and writes their name and email into the sheet for you.

Why It Matters: Every business needs a database. But databases are scary and hard to set up. Google Sheets is free, easy and you can see your data right there on the screen. I use this in almost every AI automation workflow to store information or to give the robot a "to-do list".

Google Sheets Node setting.
4. Edit Fields (Set Node), The "Label Maker"
This node used to be called "Set" and it is the Swiss Army knife of n8n.
What It Does: It organizes and cleans up your data. Imagine you have a messy pile of papers. This node lets you take one paper, erase the parts you don't need and write a new, clear title on it.
It can rename data (e.g., change "First_Name_123" to just "Name").
It can create new data (e.g., add a label that says "Status: Pending").
It can remove data you don't want (e.g., remove the “timestamp” label).
It can set data types: String, number, boolean, array, object and binary data.

Set Node setting.
Why It Matters: Computers are very picky. If one node calls it "Name" and the next node looks for "FullName", the automation breaks. The Edit Fields node ensures everything is labeled perfectly so the robot doesn't get confused.
III. How Do Logic Nodes Make Your Workflows Smart?
Answer
Logic nodes turn a straight line into a decision tree. The IF node sends items down a True or False path based on a condition, like “is this a VIP client”. The Switch node handles many branches at once, such as routing PDFs, images and text files to different flows. The HTTP Request node acts like a universal translator, letting n8n talk to any API even if there is no official node.
Key takeaways
IF = simple yes or no decisions for different handling.
Switch = clean way to send items into many different paths.
HTTP Request = connect to any API or new tool you want.
Critical insight
Once you master HTTP Request, you are not limited by n8n’s built in nodes anymore. Any tool with an API is “supported” for you.
5. IF Node, The "Fork in the Road"
This is where your AI automation starts to make decisions.
What It Does: It asks a Yes or No question. Based on the answer, it sends the data down one of two paths.
Question: "Is this email from a VIP client?"
True Path (Yes): Send a text message to the boss immediately.
False Path (No): Just save it to a spreadsheet for later.

Edit Fields Node setting.

Why It Matters: Without this, your AI automation is just a straight line. With this, your automation can be smart. It can handle different situations differently.
6. Switch Node, The "Roundabout"
The IF node only has two paths (Yes or No). But what if you have five paths?
What It Does: It is like a traffic roundabout with many exits. You give it a rule and it sends the data to the correct exit.
Rule: Check the file type.
Exit 1: If it is a PDF, go here.
Exit 2: If it is an Image, go here.
Exit 3: If it is a Text file, go here.
Exit 4: Other types.

The Workflow.

Edit Node setting.

Download File node setting.

Switch Node setting.
Why It Matters: It keeps your workflow clean. Instead of chaining ten IF nodes together (Is it a PDF? No. Is it an Image? No...), you just use one Switch node to sort everything instantly.
7. HTTP Request, The "Universal Translator"
This sounds technical but it is the most powerful node in the list.
What It Does: It allows n8n to talk to any other software in the world, even if n8n doesn't have a specific "button" for it.
Does the software have an "API"? (An API is just a way for computers to talk).
If yes, the HTTP Request node can talk to it.
Example: You want to access Perplexity but n8n doesn't have a Perplexity Node (I know it does but just ignore that for science). So, how could you use Perplexity in n8n? The answer is through the HTTP Node.
First, I go to Perplexity API Platform, let’s pick the easiest way, the “Find Results” option. Then we’ll copy the URL.

Now, we go back to n8n, add an HTTP Node and paste the URL that we just copied. The method is going to be GET because we want to get the result.

We're not done yet. There are two ways to actually connect to your own Perplexity.
The first is using the Headers section and pasting your Perplexity API key (not recommended).
The second way is better and more secure: you go to the Authentication field → Choose Generic Credential Type → then choose Header Auth in Generic Auth Type. After that, we create a new credential with the value taken from the document. We'll have a new Perplexity credential with higher security than the first method.

The First Way.

The Second Way.
The third step is turning on the “Send Body” field → choose the JSON option in the “Body Content Type” → select “Using JSON” in “Specify Body”. Now, go back to the Perplexity docs, copy this JSON and paste it into the JSON field in n8n.
{
"query": [
"What is Comet Browser?",
"Perplexity AI",
"Perplexity Changelog"
]
}
The last thing is to hit the Execute step button in n8n and see the result. You could change the question in the query field in JSON, like “Tell me anything about the AI Fire newsletter?” instead of “What is Comet Browser?”.

And that’s how you could connect Perplexity to n8n without using the Perplexity node. All by using the API key.
*One more example: this is another example of how to use HTTP Node to get a random joke from the website chucknorris.io.

Why It Matters: n8n has many built-in integrations (like Gmail or Slack). But it doesn't have everything. If you want to connect to a small, niche tool or a brand new AI service that just launched yesterday, you use this node. It connects your automation to the entire internet.
Creating quality AI content takes serious research time ☕️ Your coffee fund helps me read whitepapers, test new tools and interview experts so you get the real story. Skip the fluff - get insights that help you understand what's actually happening in AI. Support quality over quantity here!
IV. How Do Structure And Flow Nodes Control Complex Work?
Answer
Structure nodes control how work moves through a workflow. Sub Workflows let you move repeated logic into separate helper flows that you can call from many places, like a reusable research agent. Loop Over Items processes arrays one item at a time so you do not hit rate limits or crash APIs. Split Out takes a list and turns it into separate items so downstream nodes can handle each element correctly.
Key takeaways
Sub Workflows = reusable “mini robots” you can plug into many flows.
Loop Over Items = safe way to handle lists without rate limit issues.
Split Out = turn one big list into separate items for later nodes.
Critical insight
You stop thinking in “big blobs of data” and start thinking in clean, small units of work. This is how you keep large automations stable.
8. Sub-Workflows, The "Helper Robots"
Imagine you are building a house. You don't do everything yourself. You hire a plumber and an electrician.
What It Does: A Sub-Workflow is a separate, smaller automation that does one specific job. Your main workflow can "call" it to do that job and send the result back.
Example: You build a "Technical AI Agent" workflow.
Main Workflow: "Hey News Tool, look up this company".
Sub-Workflow: (Does the research) "Here is the info".
Example: My workflow starts with a chat in Telegram about news on Alphabet Inc.
After analyzing my question, the AI Agent Node (Technical AI Agent) will know that it needs to use the News Tool to get the research.
The new request will be sent to another workflow (sub-workflow) through an “Execute Sub-workflow” trigger.
It’ll send the new question to a website that researches news (through HTTP Node).
After having the answer, it will be sent back to your main workflow and given to me through a Telegram Node.

Main Workflow

Sub-Workflow
Why It Matters: It saves you from building the same thing twice. Once you build a "Research Tool", you can use it in all your automations. It makes you much faster.
If you want to build this workflow, you could see the guide right here: Technical Analyst AI Agent Workflow.
9. Loop Over Items, The "One by One"
Imagine you have a stack of 50 envelopes to sign. You don't sign them all at the exact same second. You do them one by one.
What It Does: If your automation receives a list of 100 items (like 100 emails), this node takes the first one, processes it, then takes the second one and so on.
Example: My demo workflow has 100 items that need to be processed.
After going through the "Loop Over Items” (with the batch size = 1), each item (one by one) will go to the HTTP Node.
After analyzing the result, it’ll be sent back to the Loop Node.
Here, the Loop Node does two things: one is sending the answer to the next node (Edit Fields node) and two is giving the HTTP node the next item (step by step).

The Loop Over Items setting.
Why It Matters: If you try to send 100 emails to ChatGPT at the exact same second, ChatGPT will crash or block you (this is called "Rate Limiting"). The Loop node slows things down and ensures every single item gets treated correctly without breaking the system.
10. Split Out, The "Bag of Marbles"
Sometimes, data comes in a big clump. Imagine a bag of marbles.
What It Does: The Split Out node opens the bag and dumps the marbles onto the table so they are all separate items.
Input: One "list" containing 10 names.
Output: 10 separate items, each with one name.

The Split Out Node turns a list inside the “body” field into separate items.
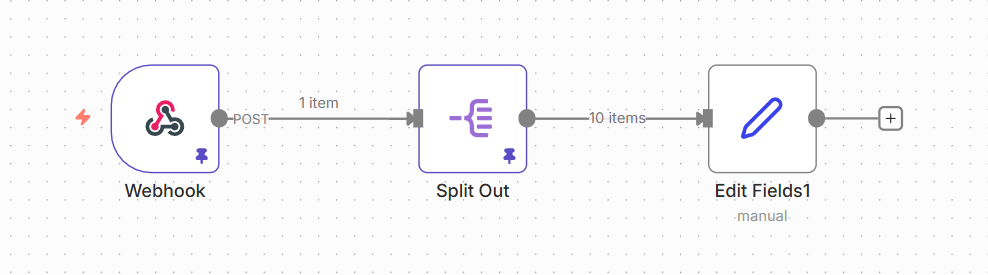
From one item (a long list) to 10 items (easy to see).
Why It Matters: Most nodes in n8n like to work on one item at a time. If you try to send a "list" of emails to the Gmail node, it might get confused and try to put all 10 email addresses into the "To" field of a single email. You want to send 10 separate emails. So, you use Split Out first to separate them.
V. Conclusion to Part 1
You now know the 10 foundational nodes of n8n that power 80% of AI automation.
You can trigger automations (Schedule, Event).
You can store and clean data (Sheets, Edit Fields).
You can make decisions (IF, Switch).
You can connect to anything (HTTP).
You can manage the flow (Sub-Workflows, Loop, Split Out).
If you stop here, you can already build amazing things. But if you want to build AI Agents (the systems that can think, reason and do complex work), you need the next 7 nodes.
In Part 2, we will cover the advanced stuff: AI Agents, Webhooks, Code and Aggregates. This is where you go from "Automation" to "Intelligence".
If you are interested in other topics and how AI is transforming different aspects of our lives or even in making money using AI with more detailed, step-by-step guidance, you can find our other articles here:
The Power of AI Automation: It Can Find and Create Viral Reels for You in Minutes!
This n8n Workflow Analyzes Crypto, Forex & Stocks Like A PRO*
*indicates a premium content, if any
How would you rate this article on AI Automation?We’d love your feedback to help improve future content and ensure we’re delivering the most useful information about building AI-powered teams and automating workflows |
Reply