- AI Fire
- Posts
- 🧩 Think AI Is Just LLMs? You're Missing These 8 Key Models
🧩 Think AI Is Just LLMs? You're Missing These 8 Key Models
Everyone calls all AI an 'LLM'. This is wrong. Learn the big difference between an LLM, VLM, SLM, and SAM. Get to know the 8 essential types for 2025.

Before you read: How many AI model types (besides LLMs) can you name? |
Table of Contents
Many people think AI is just ChatGPT. But really, the world of AI has many different types of models. It's like a toolbox with many tools. You can't use a hammer to turn a screw. If you want to understand AI better, you need to know how these models are different.
Understanding this is very helpful. You will know which tool to use for your job.
Let's learn about 8 important AI model types you should know. This article will use simple, easy-to-understand language, good for beginners.
1. LLM - Large Language Model
What Is An LLM?

This is the most famous type of AI. You can think of an LLM like a very smart friend. This friend has read every book and every website in the world. This friend can talk, write stories, write poems, and even write computer code.
They are called "Large" because they are trained on a huge (very, very big) amount of text data. They learn sentence patterns, how words connect, and how people use language.
How Does It Work (Simply)?
An LLM's main job is to guess the next word.
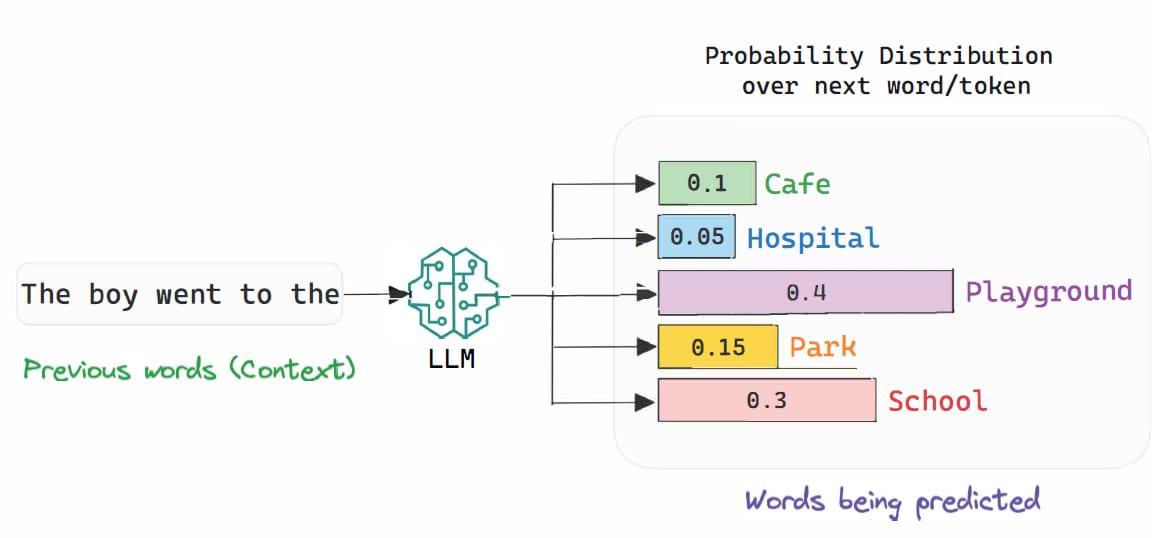
Imagine you say: "The cat climbed up the..." An LLM will try to guess the next word. Based on billions of sentences it has read, it knows the next word could be "tree" or "roof", but probably not "car". It will choose the word that is most likely to be next.
It repeats this process. Each new word helps it guess the next word. By doing this, it can write a full paragraph, an essay, or a complete answer. They "think" using "tokens", which are pieces of words. For example, the word "running" might be one token, but the word "unbelievable" might be three tokens: "un-", "believe-", and "-able".
What Is It Used For? (Use Cases)
LLMs can do many things. They are very good at jobs that use text.
Writing and creating content: You can ask it to write a blog post about why drinking water is good. It can write a professional email to ask for a day off. It can also help you think of ideas for a short story.
Programming helper: Programmers use LLMs to help them write code faster. It can find mistakes in code (debug), explain difficult code, or write a whole function from a simple description.
Customer service chatbots: Many companies use LLMs to answer common customer questions. They can understand your questions and give you answers right away, 24/7.
Translating languages: They can translate text from one language to another very well.
Summarizing text: If you have a long 20-page article, you can ask an LLM to summarize the main ideas in 3 bullet points.
Learn How to Make AI Work For You!
Transform your AI skills with the AI Fire Academy Premium Plan - FREE for 14 days! Gain instant access to 500+ AI workflows, advanced tutorials, exclusive case studies and unbeatable discounts. No risks, cancel anytime.
Example Of How To Use It (Prompt)
Here is an example of how you can ask (prompt) an LLM to get a good result.
Situation: You want to write an email to your boss to ask to work from home 3 days a week.
A bad prompt (too short):
"Write an email to work from home."Why it's bad: It's too general. Which boss? Why? When do you want to work from home? The LLM doesn't know these details.
A good prompt (specific and has context):
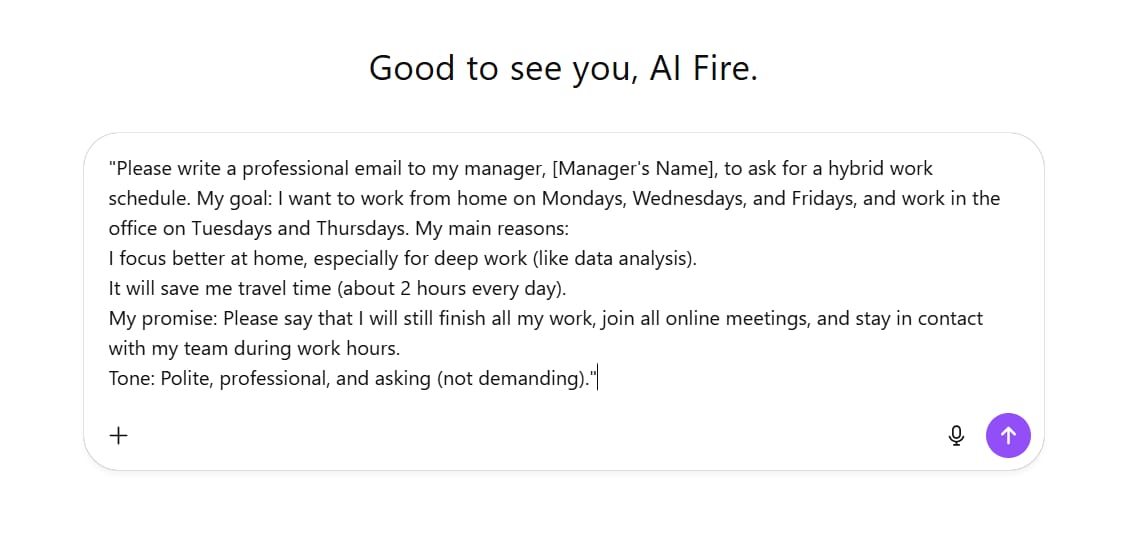
"Please write a professional email to my manager, [Manager's Name], to ask for a hybrid work schedule. My goal: I want to work from home on Mondays, Wednesdays, and Fridays, and work in the office on Tuesdays and Thursdays. My main reasons:
I focus better at home, especially for deep work (like data analysis).
It will save me travel time (about 2 hours every day).
My promise: Please say that I will still finish all my work, join all online meetings, and stay in contact with my team during work hours.
Tone: Polite, professional, and asking (not demanding)."The Result:
Here’s a clear and professional version of your email:
---
**Subject:** Request for Hybrid Work Schedule
Hi [Manager’s Name],
I hope you’re doing well. I’d like to request a hybrid work schedule where I work from home on **Mondays, Wednesdays, and Fridays**, and come to the office on **Tuesdays and Thursdays**.
Working from home helps me focus better on deep work tasks like data analysis and also saves around two hours of commute time each day.
I’ll make sure to:
* Complete all my work on time
* Join every online meeting
* Stay in contact with the team during work hours
Please let me know if this arrangement could work or if you’d like to discuss it further.
Best regards,
[Your Name]
---
Would you like me to make it sound slightly **more formal** (for a corporate manager) or **more friendly** (for a startup-style tone)?What To Watch Out For?
LLMs are not perfect. They have a big problem called "hallucination".
This means they can make up information confidently. They might name a study that doesn't exist, or say a historical fact that is wrong. They don't "know" the truth; they only "guess" the next word that looks correct. So, you must always check important information they give you. Also, they cost a lot of money to run and need very strong computers.
2. LCM - Latent Consistency Model
What Is An LCM?
If LLMs are about text, then LCMs are about pictures.
Have you ever used an AI image creator and had to wait 30 seconds or 1 minute for a picture? That's because old image models (like Stable Diffusion) work in many steps. They start from a "messy" picture (called noise) and slowly "clean" it in 50 or 100 steps to make the final image.
LCM is a new way to do this much faster. It can make high-quality pictures in just a few steps (like 2 to 8 steps). This makes them great for apps that need speed.
How Does It Work (Simply)?
Imagine you are drawing a picture.
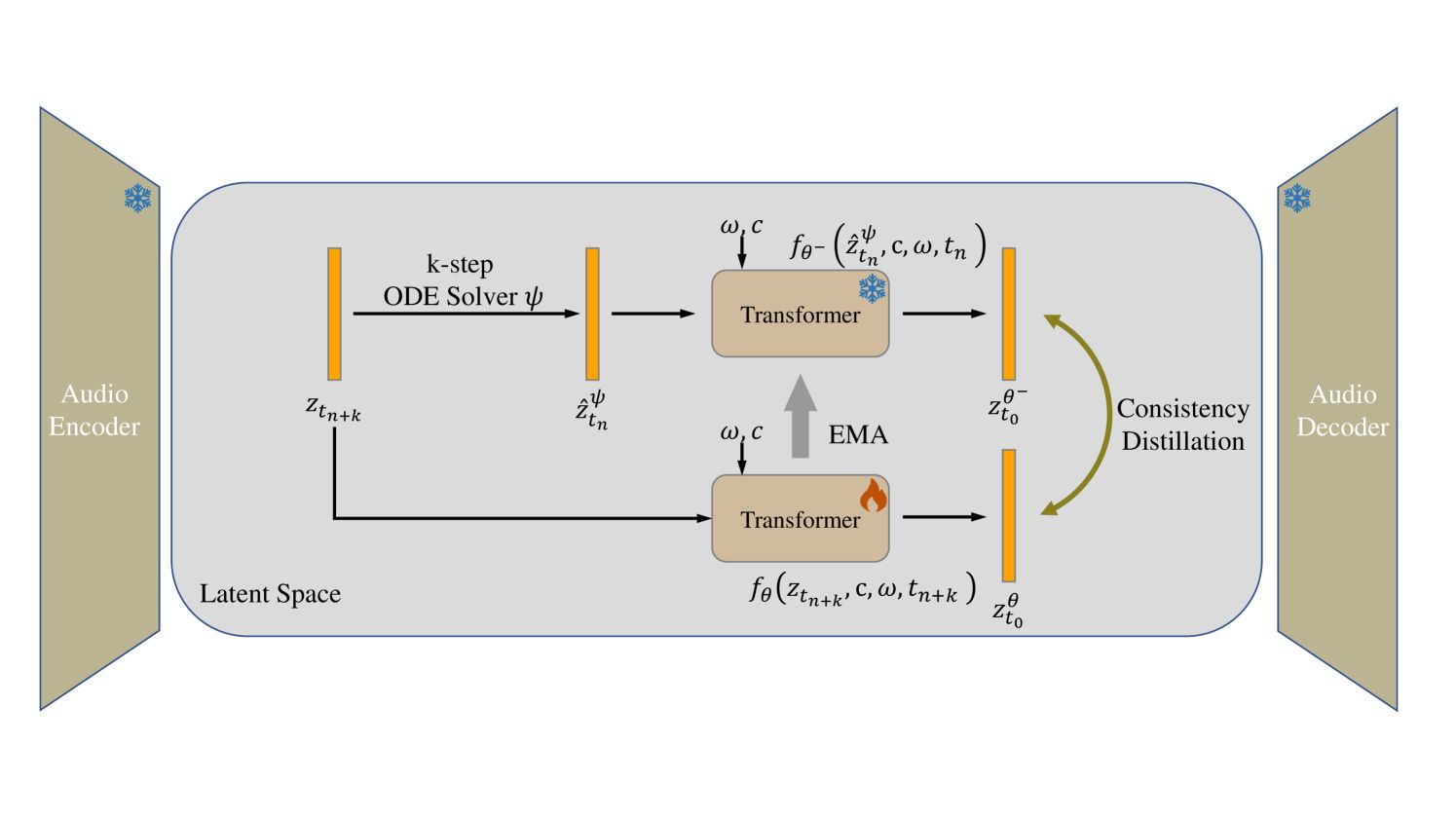
Old model (Diffusion): Like a careful painter. They draw one line, stop, look, draw the next line, stop, look... 50 times. Very slow.
LCM model: Like a master painter. They look at the blank paper and know exactly what the final picture will look like. They just need a few main strokes, and the picture appears.
LCMs learn to "jump" steps. Instead of going step-by-step, it learns to go from step 1 straight to step 10, then from step 10 to step 30, and then finish. It does this by learning "consistent patterns" in a compressed space (called the "latent" space).
What Is It Used For? (Use Cases)
Because LCMs are so fast, they are great for anything that needs results right away.
Making pictures on your phone: Photo editing apps on your phone can use LCMs to make AI filters or avatars without sending your data to the cloud.
AR/VR applications: When you are wearing a VR headset, everything needs to change in real-time as you turn your head. LCMs can help create virtual worlds and objects quickly.
Fast design tools: This helps designers try many different visual ideas very quickly. They can type an idea and see the picture almost instantly.
Making videos look better: LCMs can be used to improve video quality in real-time, for example, in video calls.
Example Of How To Use It (Prompt)
You usually use an LCM inside a picture tool. You don't "talk" to it. You will see it in the settings of the tool (for example, choosing "LCM" as the sampler).
Situation: You are using a picture-making tool and want to make a picture fast.
LCM Setting (fast):
Prompt:
"An astronaut riding a horse on Mars, oil painting."Sampler: LCM
Steps: 5
Result: The LCM setting will give you a picture almost instantly, while the other setting takes much longer. The quality might be a little different, but the speed is much faster.

What To Watch Out For?
Speed is the main benefit, but it's sometimes a trade-off. Some users feel LCMs might not be as detailed as the slower methods (with 100 steps). It might miss small details or make the picture look a bit too "smooth". But this technology is getting better very fast.
3. LAM - Language Action Model
What Is A LAM?

If an LLM is a smart friend (who only talks), a LAM is a smart assistant (who does things).
A LAM is the next step. It doesn't just understand your words; it takes action based on your words. This is the brain behind "AI agents".
Think about the difference:
You tell an LLM: "How do I book a flight to Da Nang?"
The LLM answers: "You should go to the Vietnam Airlines website, choose your dates, and fill in your information..." (It only talks).
You tell a LAM: "Book me the cheapest round-trip flight to Da Nang for next weekend."
The LAM answers: "OK. I found a VietJet Air flight for 2,500,000 VND. Do you want me to confirm the booking?" (It does).
How Does It Work (Simply)?
A LAM combines many things:

An LLM (the brain): To understand what you want.
Memory (a notebook): To remember who you are, what you said before, and what your final goal is.
A Planner (a map): To break a big task into small steps. For example: "Book a flight" = 1. Check calendar -> 2. Open browser -> 3. Go to airline website -> 4. Search for flights -> 5. Report back to the user.
Ability to use tools (hands and feet): This is the important part. A LAM can connect to other tools, like your web browser, your calendar, your email, or other services (called APIs).
It is like a project manager. It understands the goal, makes a plan, and then does the work itself or tells other tools to do it.
What Is It Used For? (Use Cases)
LAMs are the future of personal and work automation.
AI Agents: These are tools like Cognition (an AI programmer) or agents from Zapier. You can give it a job like: "Find 10 potential customers in the F&B industry in HCMC, write an email to introduce our product to them, and show me the draft."
Digital Assistants: An assistant that can access apps on your phone. You say: "When I get home, turn on the living room lights, play relaxing music, and set an alarm for 6 AM tomorrow."
Advanced Customer Support Bots: Instead of just answering questions, this bot can actually solve problems. For example: "I want a refund for order #12345." The LAM bot can go into the system, check the order, process the refund, and send a confirmation email.
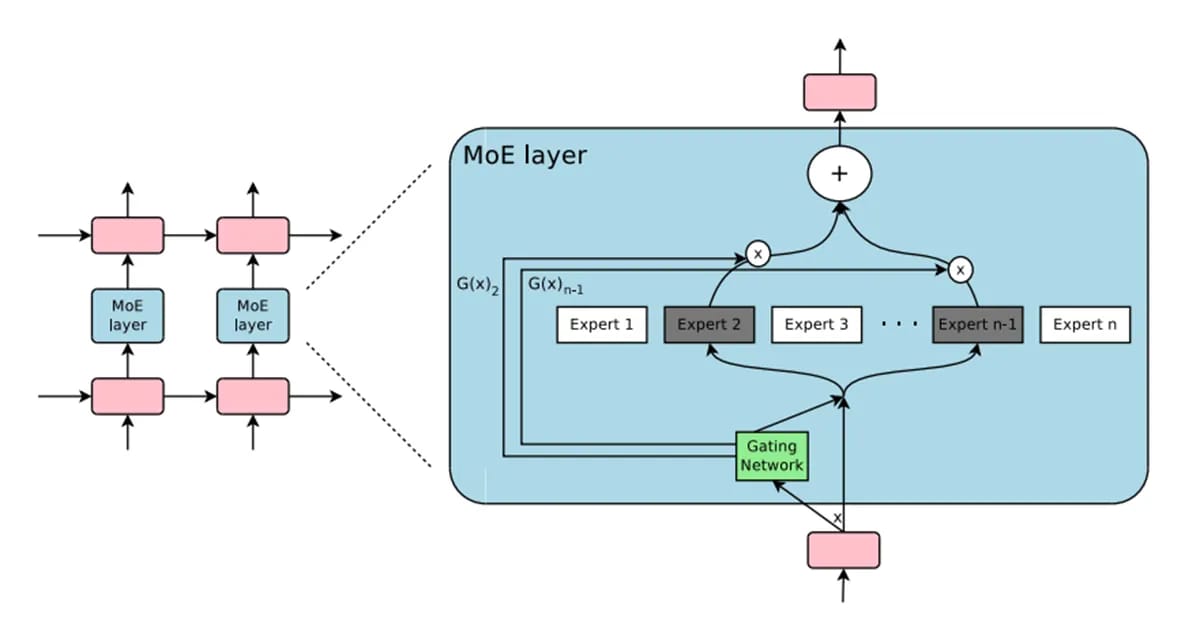
4. MoE - Mixture Of Experts
What Is An MoE?

Imagine you have a very hard question. Instead of asking one person who knows everything (like an LLM), you ask a group of experts.
If you ask about medicine, the doctor expert will answer.
If you ask about history, the historian expert will answer.
If you ask about programming, the code expert will answer.
That is an MoE. This is not a single model, but a system of many small models (called "experts").
Big models like Mixtral from Mistral AI and (people believe) GPT-4 use this MoE structure.
How Does It Work (Simply)?
An MoE system has two main parts:
The Experts: These are many smaller AI models. Each expert is trained to be very good at one thing. For example, an expert for poetry, an expert for math, an expert for Japanese.
The Router: This is a "manager" AI. When you give it a prompt (a question), the "Router" looks at it and decides: "Ah, this question is about programming and a little bit of data. I will send it to Expert #5 (code) and Expert #8 (math) to handle this."
It doesn't use all the experts at once. It only picks the best 1 or 2 experts for the job. This makes the model very efficient.
What Is It Used For? (Use Cases)
The biggest benefit of MoE is size and efficiency. You can build a giant model (e.g., 1000 billion parameters) but when it runs, it only costs as much as a small model (e.g., 100 billion parameters), because it only uses a few experts at a time.
Top-tier LLMs: This is how companies create the strongest AI models in the world. They can know so many things because they have hundreds of experts inside.
Multilingual systems: You can have separate experts for Vietnamese, English, Japanese. When you type in Vietnamese, the "Router" sends it to the Vietnamese expert.
Personalization: A company can create its own experts trained on its private data (e.g., an expert on company law, an expert on company products) and add them to the MoE model.
Example Of How To Use It (Prompt)
You don't "command" an MoE directly. You still use it like a normal LLM. But when you ask a complex question, the MoE will work better than a normal LLM of the same size.
Situation: You ask a question that needs many types of knowledge.
Prompt:
"Please explain the concept of 'inflation' in economics, and write a small Python code to calculate the yearly inflation rate from a list of monthly CPI numbers."
The Result:
def yoy_inflation_series(cpi):
"""cpi: list of monthly CPI values in order.
returns list of 12-month (% YoY) rates for months 13..end"""
return [ (cpi[i]/cpi[i-12] - 1) * 100 for i in range(12, len(cpi)) ]
def latest_yoy_inflation(cpi):
"""% YoY for the most recent month"""
if len(cpi) < 13: raise ValueError("Need ≥13 months of CPI")
return (cpi[-1]/cpi[-13] - 1) * 100
# Example
cpi = [100.0, 100.2, 100.4, 100.6, 100.9, 101.1, 101.3, 101.6, 101.8, 102.1, 102.4, 102.7,
103.0, 103.3, 103.6] # replace with your CPI
print("Latest YoY inflation (%):", latest_yoy_inflation(cpi))
print("Series (%):", yoy_inflation_series(cpi))What happens inside the MoE: The "Router" sees this. It will activate:
The Economics Expert (to explain "inflation").
The Python Programming Expert (to write the code).
The final answer combines the information from both experts, making a very high-quality answer.
What To Watch Out For?
Training MoE models is very complex. Deciding which expert the "Router" should send the question to is a hard problem. If the "Router" picks the wrong expert, the answer will be bad. Also, they need a lot of memory (VRAM) to hold all the experts, even if they aren't all being used.
5. VLM - Vision Language Model
What is a VLM?
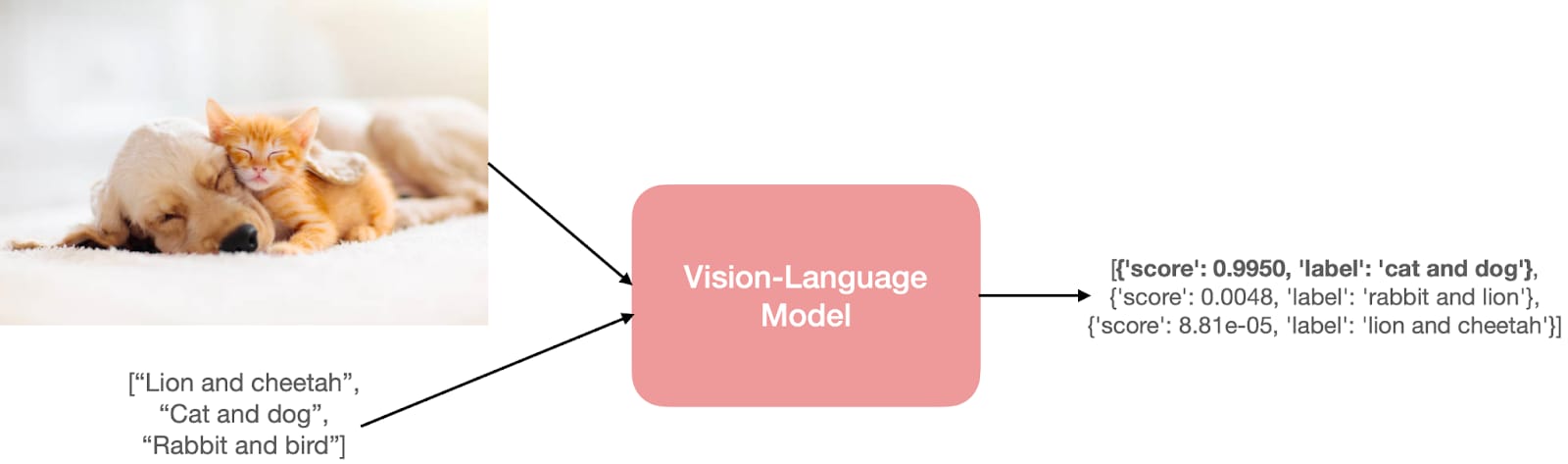
A VLM is an AI model that can see and talk. It understands both pictures and text at the same time.
This is a big step. Old LLMs were "blind" - they could only read words. VLMs have "eyes". Models like Gemini from Google and GPT-4o from OpenAI are the most famous VLMs.
You can upload a picture and ask questions about it. You can show it a video and ask it to summarize.
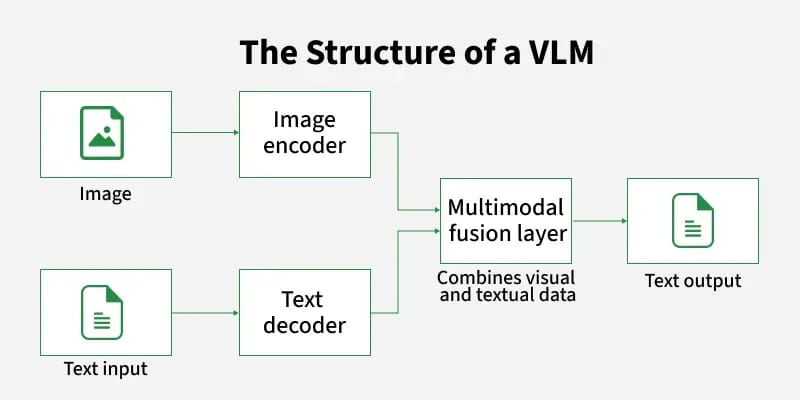
How Does It Work (Simply)?
A VLM has two parts of its brain working together:
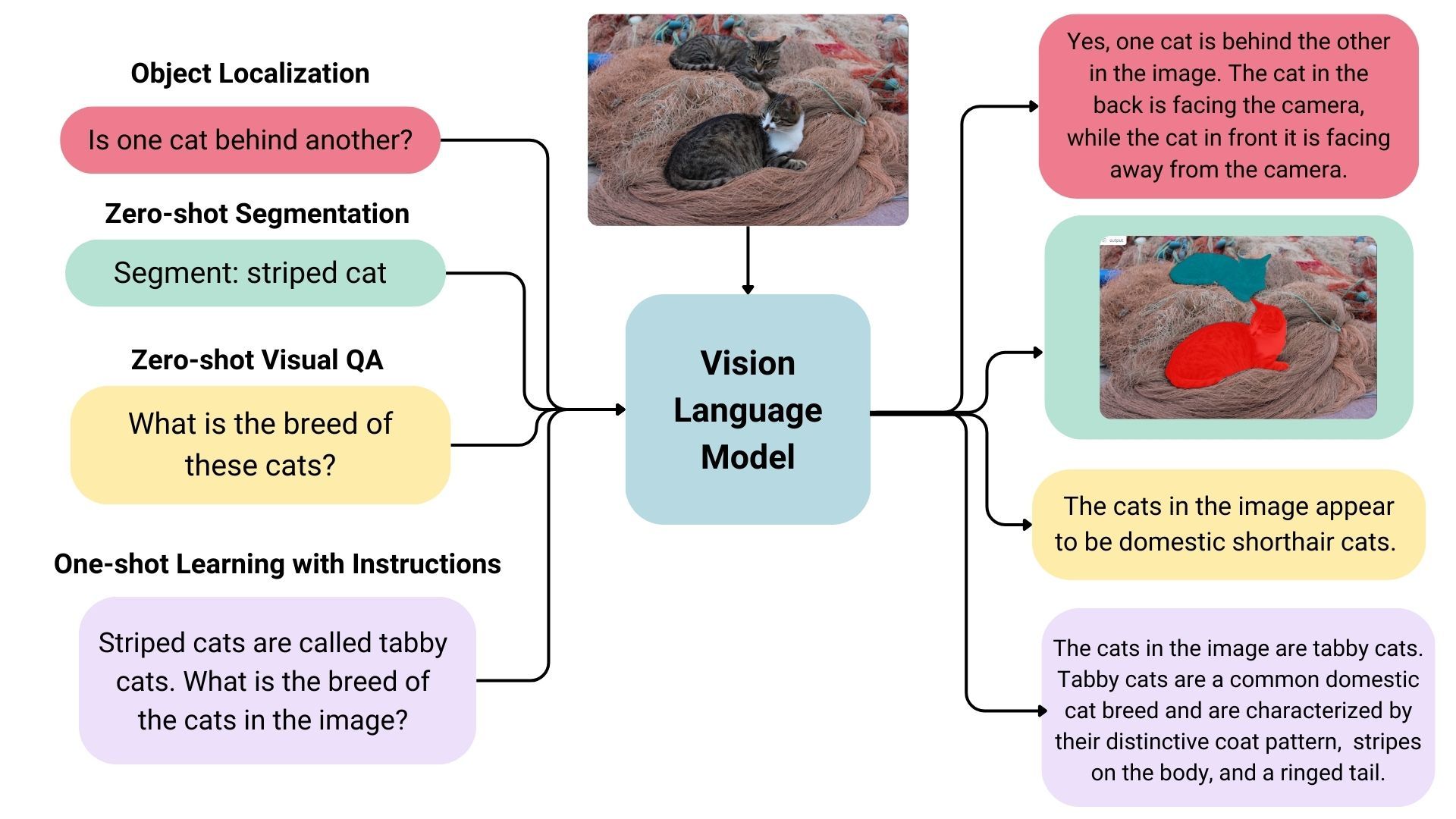
An Image Encoder (The Eyes): A part of the AI trained to look at a picture and turn it into a string of numbers. This string of numbers describes what is in the picture (e.g., "there is a cat", "it is orange", "sitting on a chair").
A Language Model (The Mouth): A normal LLM.
The magic happens when they connect these two parts. The language model learns that the string of numbers "describing the cat" means the same thing as the words "an orange cat sitting on a chair".
So, when you give it a picture and ask: "What is this?", its "eyes" analyze the picture, turn it into numbers, and its "mouth" will look at those numbers and say, "That is an orange cat."
What Is It Used For? (Use Cases)
Being able to understand both worlds (pictures and text) opens up many uses.
Multimodal Assistants: You can take a picture of your fridge and ask, "What can I cook tonight with these things?" The VLM will see (eggs, tomatoes, onions) and suggest (scrambled eggs).
Search with pictures: You can search for things that are hard to describe. For example, you take a picture of a pair of shoes you see on the street and ask, "Where can I buy these shoes?"
Tools for visually impaired people: A VLM can describe the world to a blind person through their phone. ("You are walking towards a closed door," "The person in front of you is smiling.").
Video analysis: Summarize a long lecture or a video meeting.
Example Of How To Use It (Prompt)
With a VLM, your prompt includes both pictures and text.
Situation: You are trying to fix a broken bicycle and you take a picture of the broken part.
Prompt:
(Upload picture): [Picture of a bicycle chain that fell off]
(Text):
"This is my bike. I don't know much about fixing bikes. What is this called and how do I fix it?"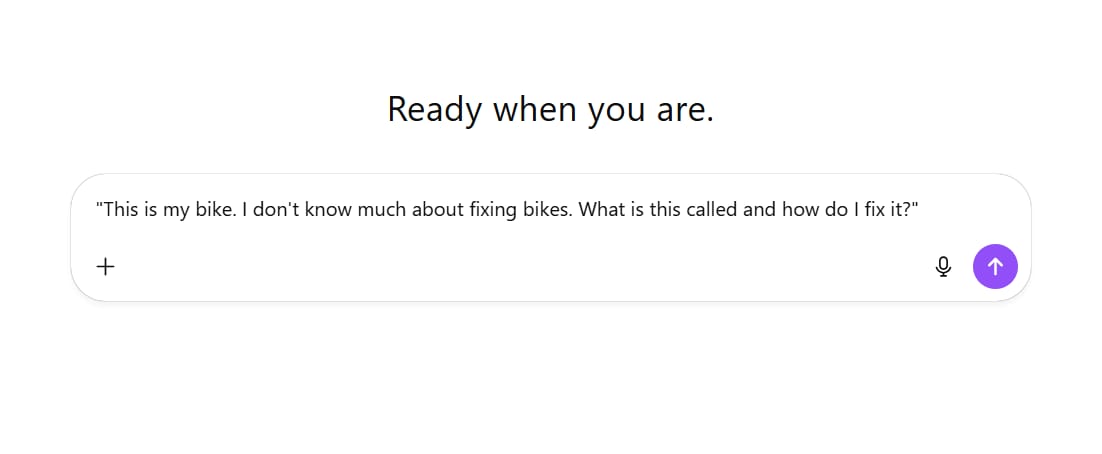
VLM's Answer: "This is your bicycle chain, and it looks like it has fallen off the gear. To fix it, you should wear gloves, pull the derailleur (the gear-changing part) back to make the chain loose, then carefully put the chain back on the smallest gear and slowly turn the pedals."

What To Watch Out For?
VLMs can also "hallucinate" (make things up). It might see an object wrongly or describe an action in a picture incorrectly. They are also more complex and expensive than LLMs. There are also privacy worries when you upload pictures of faces or your home.
6. SLM - Small Language Model
What Is An SLM?
While everyone is racing to make "large" models (LLMs), another group is focused on making "small" models (SLMs).
An SLM is a language model that is small and efficient. They are designed to run on weaker devices like mobile phones, laptops, or even smart devices in your home.
Models like Microsoft's Phi-3 or the small versions of Llama 3 are good examples.
How Does It Work (Simply)?
An SLM is also a next-word-guesser, like an LLM. But they are made differently:
Fewer parameters: If an LLM has 1000 billion "nodes" (parameters), an SLM only has 1 or 3 billion. Fewer parameters mean it needs less memory and computing power.
High-quality data: Instead of feeding the whole internet to the model, researchers make SLMs by feeding them "textbook-quality" data. They focus on quality, not quantity.
The result is a small model that is very smart, especially in specific areas like logic or coding.
What Is It Used For? (Use Cases)
SLMs are very important because they let AI run everywhere, without needing a strong internet connection.
On-device AI: This is the biggest use.
Phone Assistants: Your phone's assistant can understand and answer you instantly without sending your data to the cloud.
Privacy: Because your data (your emails, your messages) never leaves your phone, it is much safer.
Smart Devices (IoT): Your car can have an SLM to understand your voice commands, or your smart microwave can understand "reheat for 30 seconds."
Coding tools: Your code editor (IDE) can run an SLM locally to autocomplete your code instantly, with no delay.
What To Watch Out For?
They are "small", so they "know less". They might not know about uncommon historical events or very specific topics. Their memory is also shorter; they might forget what you said at the start of the conversation faster.
7. MLM - Masked Language Model
What Is An MLM?
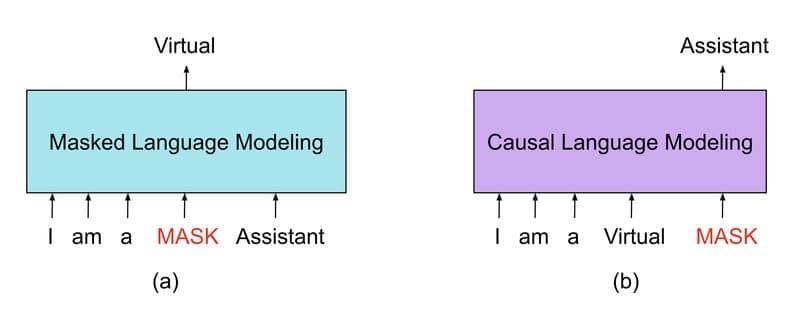
This is an "older" type of model, but it is very important. MLM is the foundation for how Google Search understands you. The most famous model is Google's BERT.
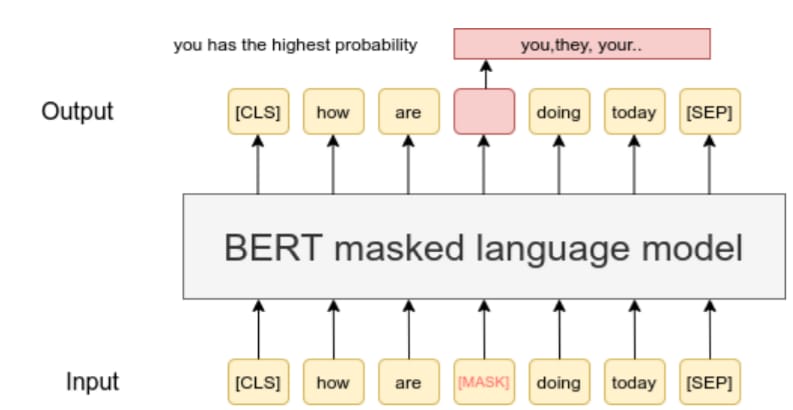
Unlike LLMs (which guess the next word), an MLM is like a fill-in-the-blank game.
You give it a sentence: "The weather today is [MASK] beautiful." The MLM's job is to guess the [MASK] word. In this case, it will guess "very" or "so".
How Does It Work (Simply)?
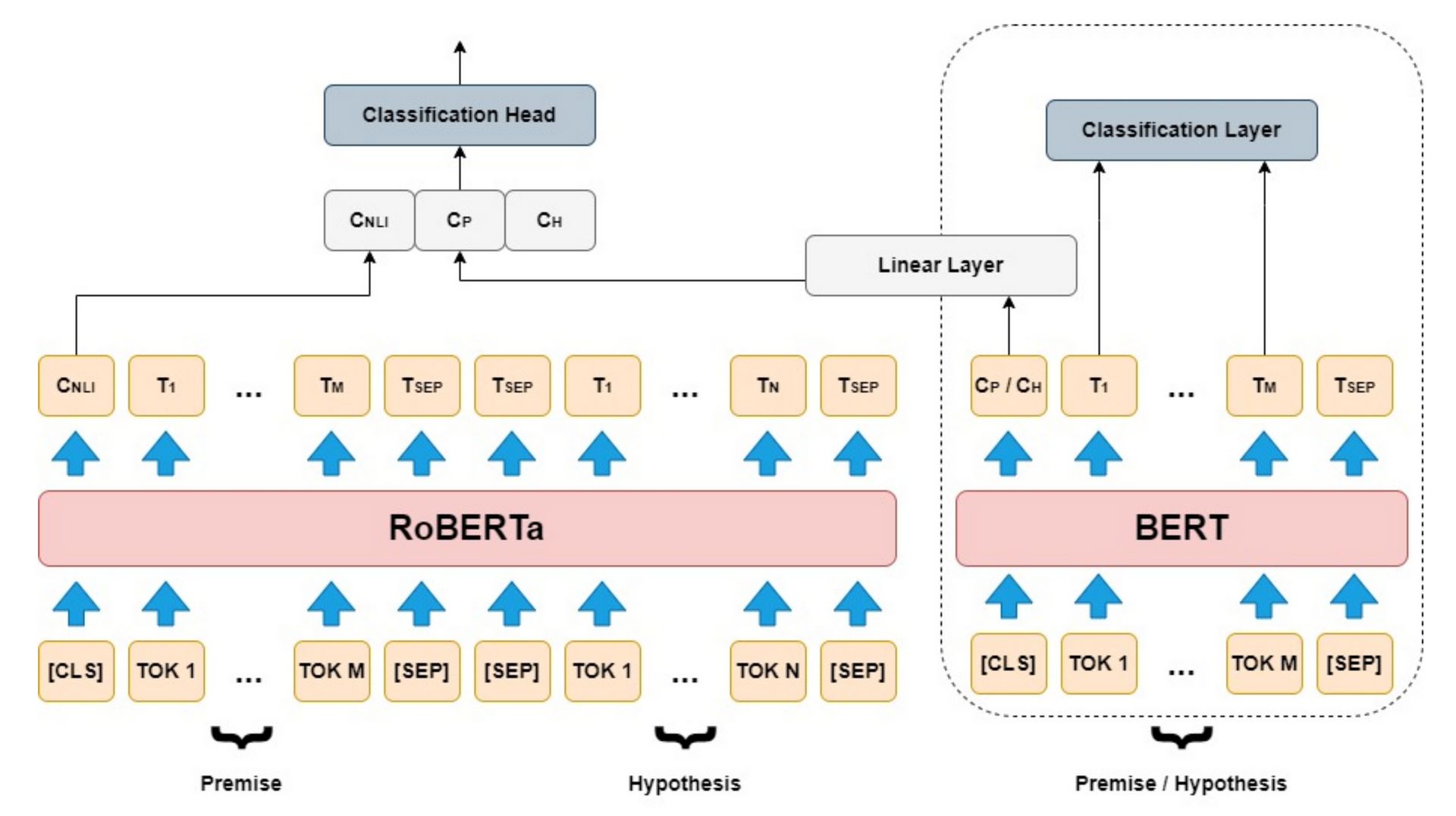
An MLM is trained by taking billions of sentences, "masking" (hiding) about 15% of the words, and then forcing the model to guess the hidden words correctly.
To do this, the model must learn to look at both the left and right side of the masked word.
In the sentence: "I took my [MASK] to the doctor because he was sick."
To guess [MASK], the model must look left ("I took my...") and right ("...to the doctor"). It will understand the hidden word could be "son," "husband," or "dog."
This ability to look both ways (bidirectional) makes MLMs understand the context (the situation) of a sentence very deeply.
What Is It Used For? (Use Cases)
MLMs are not good at writing or chatting (because they were not trained to guess the next word). Instead, they are very good at understanding meaning.
Search Engines (Google): When you search for "how to make coffee A to Z", Google (using a BERT-like model) understands that "A to Z" means "a complete guide for beginners". It understands the meaning behind the words.
Sentiment Analysis: Businesses use MLMs to read thousands of customer comments and sort them as "positive", "negative", or "neutral".
Named Entity Recognition (NER): Finding specific information in a text. For example, reading a contract and automatically pulling out the "Company Name", "Date", and "Money Amount".
What To Watch Out For?
As we said, they are not creative tools. You cannot ask BERT to write a poem. They are analysis models, not creation models.
8. SAM - Segment Anything Model
What Is SAM?

Let's go back to pictures. SAM is a very special computer vision model from Meta (Facebook).
It does not identify what is in the picture (like saying "this is a cat"). Instead, it draws an exact outline around everything in the picture.
It can "segment" (divide) a picture into individual objects. It's like the "Magic Wand" or "Quick Selection" tool in Photoshop, but fully automatic and very precise, down to the pixel.
How Does It Work (Simply)?
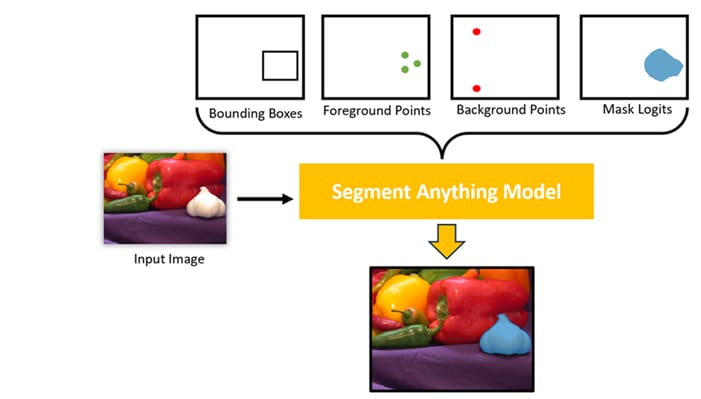
SAM was trained on a giant dataset of over 1 billion "masks" (outlines) on 11 million pictures. It has learned how to "see" objects, no matter what they are.
It doesn't need to know if it's a "table" or "chair". It just knows "this is an object" and "this is its outline".
You can interact with it by:
Clicking: You just click one point on the cat, and SAM will automatically draw the outline around the whole cat.
Drawing a box: You draw a box around the tree, and SAM will create a precise outline of that tree.
Automatic: You can also ask it to "Find everything" and it will automatically draw outlines for every object in the picture.
What Is It Used For? (Use Cases)
SAM is a foundation tool, like a LEGO brick, that can be used to build other complex apps.
Photo and Video Editing: This is the most obvious use. It's the technology behind "remove background" tools. Video editors can use it to select a person and change their shirt color in an entire video.
Medical Image Analysis: Doctors can use SAM to draw exact outlines around tumors or organs in MRI or X-ray scans. This helps measure the size more accurately.
Robots and Self-Driving Cars: For a robot to pick up an apple, it first must see the outline of the apple to know how to grab it. SAM helps robots understand the edges of objects.
Scientific Research: Scientists can use it to count cells under a microscope or track animals in satellite images.
What To Watch Out For?
SAM is very good at finding outlines, but it doesn't tell you what the object is. It will draw an outline around the dog and its bowl, but it won't tell you "this is a dog" and "this is a bowl". It just says "this is object 1" and "this is object 2". That is why it is often used with other models (like VLMs) so it can both see and understand.
Conclusion: Use The Right Tool For The Right Job
The AI world is much bigger than just one type of model.
Want to write a blog post? Use an LLM.
Want AI to run on your phone with no internet? Use an SLM.
Want an assistant to book your meetings? You need a LAM.
Want to know what's in a picture? Use a VLM.
Want to remove the background from a photo? Use a SAM.
Each model is a special tool. By understanding this basic difference, you won't be confused anymore and can use AI's power in a smarter, better way.
If you are interested in other topics and how AI is transforming different aspects of our lives or even in making money using AI with more detailed, step-by-step guidance, you can find our other articles here:
How clear were the explanations about LLMs in this article? |
Reply