- AI Fire
- Posts
- 🧠 How I’d Learn n8n From Zero In 2026. The Only 10-Minute n8n Guide You Need To Fix 90% Mistakes
🧠 How I’d Learn n8n From Zero In 2026. The Only 10-Minute n8n Guide You Need To Fix 90% Mistakes
Forget flashy agents. The real money is in standard workflows. Master the three layers of n8n and build resilient systems that run while you sleep.

TL;DR
To master AI Automation with n8n in 2026, you must prioritize standard workflows and data fundamentals over complex AI agents. Success comes from understanding how to structure JSON and logic before adding intelligence.
Beginners often struggle by skipping foundational skills like APIs and error handling. This guide provides a step-by-step roadmap through three distinct layers of automation complexity. You will learn to move from simple rule-based tasks to advanced context-aware systems while avoiding common pitfalls.
Key points
Standard workflows without AI can reduce labor costs by up to 40%.
Avoid building complex agents before mastering basic data structure and logic.
Always diagram your process on paper before opening the workflow editor.
Critical insight
Reliable automation requires robust error logging and context engineering, as clients value consistent business outcomes over sophisticated but unstable technology.
What is stopping you from mastering AI Automation? 🛑 |
Table of Contents
Introduction
If you scroll social media right now, you’ll see nonstop demos of ‘AI agents’ doing everything. You see videos of bots talking to each other, handling entire businesses, and doing magic tricks. It makes you feel like you need to jump straight into the deep end to catch up. But if you want to truly master AI automation, starting with complex agents is actually the biggest mistake you can make.
I have been down that road. When I started my journey with n8n, I tried to run before I could walk. I copied complex templates I didn't understand, got frustrated when my JSON data broke, and spent nights debugging systems that were too advanced for my skill level. I wasted months.
If I could go back, I would skip the complexity and focus on mastering the 10 essential n8n nodes first, because I eventually realized that just a handful of core tools are responsible for powering the vast majority of successful AI automations.
If you scroll social media right now, you’ll see nonstop demos of ‘AI agents’ doing everything. It makes you feel like you need to jump straight into the deep end. While I have shared how to reach the level where you can build a $3k/mo business using new AI agents, you cannot sustain that level without a solid foundation. Jumping straight into complex agents is actually the biggest mistake you can make.
Part 1: Why Is Understanding The Basics Super Important For Any Career?
Beginners often rush to build complex autonomous agents (Layer 3) without mastering foundational workflows (Layer 1), leading to fragile systems that constantly break. Success starts with learning "deterministic" automation - boring, rule-based tasks like moving data from a form to a spreadsheet which form the reliable concrete foundation of any advanced system. Only after mastering these rules should you add AI assistance (Layer 2) and finally autonomous decision-making.
Key takeaways
Structure: Automation has three layers: Standard (Rules), AI-Assisted (Smart Tasks), and Autonomous (Agents).
Fact: Simple rule-based workflows can save businesses 20–40% in labor costs.
Contrast: Layer 1 is predictable (Input A = Output B); Layer 3 is non-deterministic and hard to control.
Action: Build a solid foundation of standard workflows before attempting to deploy AI agents.
You can build a six-figure business just by mastering "boring" standard automations because most companies still do them manually.
Before we touch any AI model, we need to talk about foundations. Imagine you are building a skyscraper. You would not start with the penthouse suite, right? You start with the concrete foundation. The same logic applies here.
Most rush to the top layer (AI Agents) without understanding the bottom layers. This is why their automations break constantly. To succeed in AI automation, you must understand the three layers you’ll run into.
Layer 1: The Foundation Of Standard Workflows
This is where you must start. These are "boring" automations, but they are the most profitable and reliable. A standard workflow is "deterministic." That is a fancy word meaning: if you put input A in, you will always get output B out. It never changes.
Think about a process in a typical office:
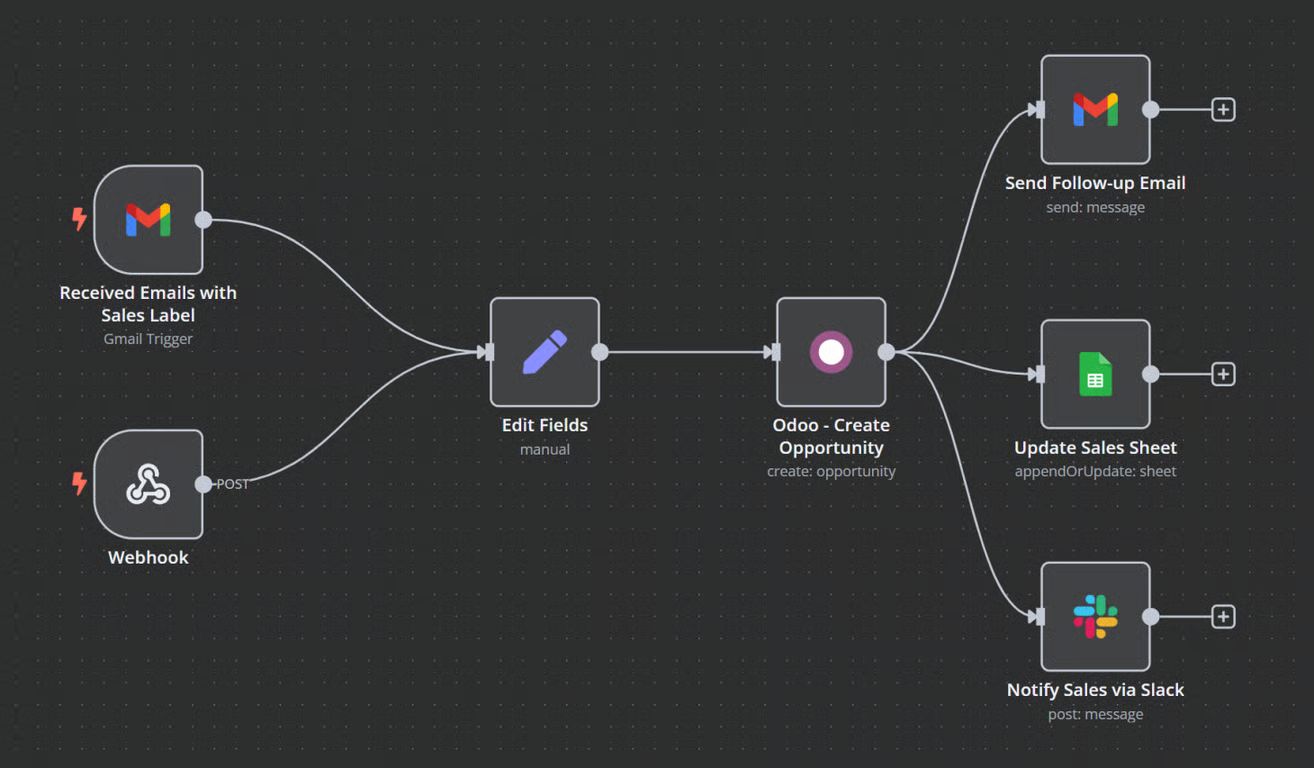
A customer fills out a form on a website.
The data goes to a Google Sheet.
A welcome email is sent via Gmail.
A notification pops up in Slack.
There is no AI here. It is just rules. But research shows that these standard workflows can save companies 20-40% in labor costs. Mastering this logic of moving data is actually the prerequisite that allows you to eventually build advanced RAG agents for pennies instead of paying for expensive tools. Like I said before, you can build a six-figure business just by mastering this layer because most companies still do this manually.
Layer 2: The Power Of AI-Assisted Workflows
Once you master the rules, you can add in some intelligence. This is the sweet spot for most businesses right now. You still have a rigid, predictable structure, but you use AI for specific tasks inside that structure.
For example, the customer fills out the form (standard), but then you use ChatGPT to analyze their message and decide if they are "angry" or "happy" (AI-assisted). To ensure this categorization is accurate, you need a model that follows instructions perfectly, which is why I recently tested GPT-5.2 against Gemini and Claude to see which one is actually reliable enough for these production workflows.
Learn How to Make AI Work For You!
Transform your AI skills with the AI Fire Academy Premium Plan - FREE for 14 days! Gain instant access to 500+ AI workflows, advanced tutorials, exclusive case studies and unbeatable discounts. No risks, cancel anytime.
Layer 3: The Complexity Of Autonomous AI Agents
This is the top level. Here, the AI decides what to do next. It has memory, it uses tools, and it plans its own path. It is "non-deterministic," meaning the result might be different every time you run it.
While this is exciting, it is hard to control. If you don't know how to fix a basic JSON error in Layer 1, you will be completely lost when an Agent in Layer 3 hallucinates or fails. Master the boring stuff first. It makes the cool stuff possible.
Part 2: What Emotional Stages Will You Face When Learning AI Automation?
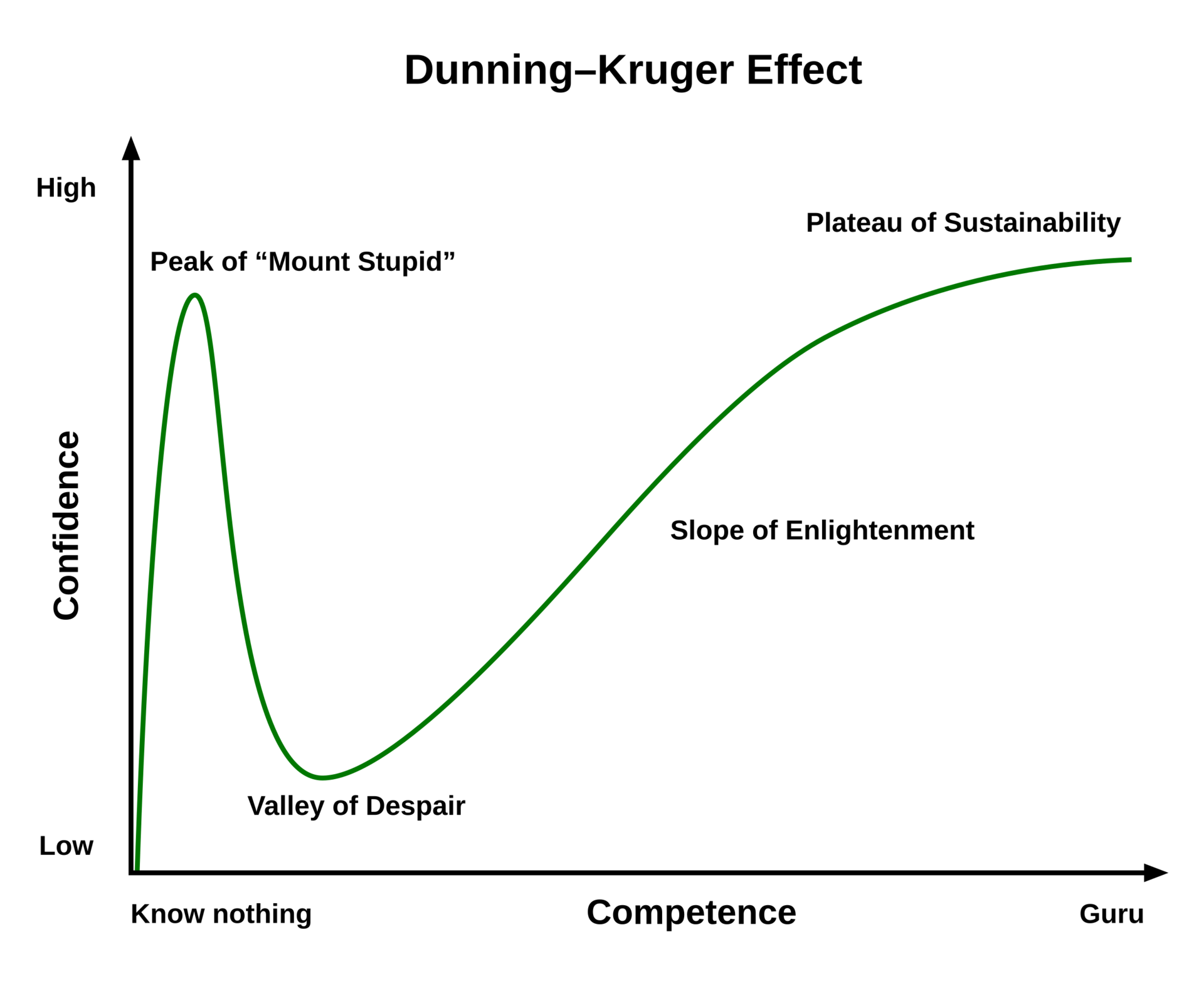
Learning AI automation follows the Dunning-Kruger curve, starting with "Uninformed Optimism" where everything looks easy, followed by a crash into the "Valley of Despair" when real technical challenges arise. This emotional low point is where most people quit, feeling not smart enough to solve basic errors. Pushing through this phase leads to "Informed Optimism," where true competence and confidence are built through solving actual problems.
Key takeaways
Stage 1: Uninformed Optimism – excitement from watching easy tutorials.
Stage 3: Valley of Despair – the critical point where most beginners quit due to errors.
Fact: Fixing a single bug is often the turning point from despair to genuine skill.
Action: Expect the crash in confidence so you don't give up when it happens.
The "Valley of Despair" is not a sign of failure; it is the necessary toll booth on the road to expertise.
Learning AI automation is not a straight line up. It is a rollercoaster. Knowing this ahead of time is your secret weapon because it keeps you from quitting when things get hard.
People often describe this with the Dunning-Kruger curve: early confidence, then the crash, then real skill. Here is what you will feel:

Just like this movie, so many emotions…
1. The Uninformed Optimist
You watch a YouTube video about an AI agent that makes money while you sleep. You think, "Wow, this looks easy! I can do this this weekend." Your confidence is high, but your competence is low. You are excited to start AI automation.
2. The Informed Pessimist
You open n8n for the first time. You see a red error message. You realize you don't know what an "Array" is. The AI isn't doing what you told it to do. Suddenly, you realize this is actually really hard. Your confidence crashes.
3. The Crisis Of Meaning (The Valley Of Despair)
This is the bottom. You feel like you are not smart enough. You think, "Maybe I should just stick to my old job." Most people quit here. They go back to watching tutorials but never build anything again.
But if you push through and fix that one error or read that one documentation page, you start to climb out.
4. The Informed Optimist
You fixed the bug. The workflow ran successfully. You understand why it broke and how you fixed it. You are not blindly confident anymore; you are confident because you have the skills. This is where you become a real AI automation expert.
Part 3: Which Core Technical Skills Do You Need For AI Automation?
Now, let's look at the toolbox. You do not need to be a software engineer with 10 years of experience, but you do need to speak the language of data. Most automation is just moving data from A to B without messing it up.
Skill 1: JSON (JavaScript Object Notation)
Don't let the name scare you. JSON is just a way to organize text so computers can read it. It looks like a grocery list.
Imagine a user profile. In plain English, you say: "John Doe is 30 years old and likes coding."
In JSON, it looks like this:
{
"name": "John Doe",
"age": 30,
"hobbies": ["coding", "reading"],
"is_active": true
} That is it. It uses "Keys" (like name) and "Values" (like John Doe). When you learn AI automation, you spend a lot of time picking specific values from a list like this. You need to know that if you want John's age, you ask for age. If you understand this structure, you can handle data from any app in the world.
Skill 2: APIs (Application Programming Interfaces)
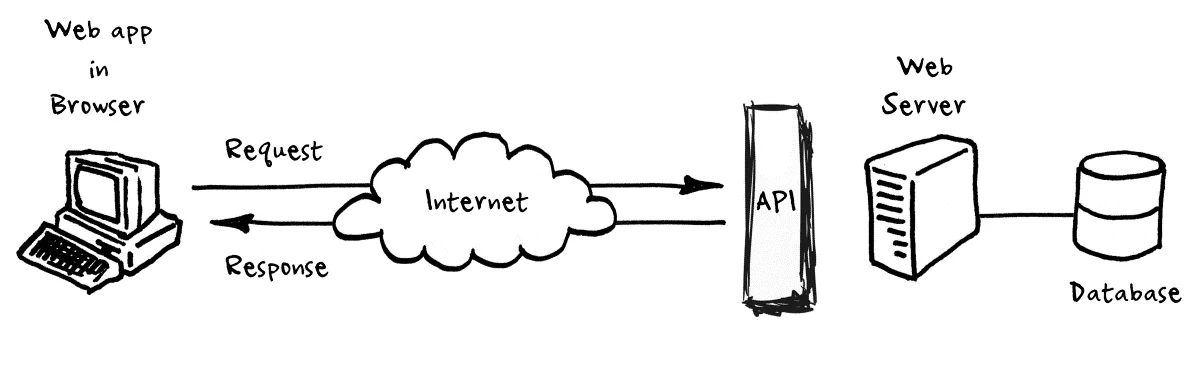
APIs are the tunnels that connect different apps. n8n has many built-in nodes (like a dedicated Google Sheets node), but real power comes when you can connect to anything.
Think of an API like a waiter in a restaurant.
You (The Client): You look at the menu (Documentation) and tell the waiter what you want.
The Waiter (The API): Takes your request to the kitchen.
The Kitchen (The Server): Prepares your data.
The Waiter: Brings the data back to you.
You don't need to know how to cook (how the server works); you just need to know how to order from the menu. Tools like Postman or simply asking Claude to "write an API request for this documentation" can bridge this gap for you.
Skill 3: Webhooks
An API is you asking for data. A Webhook is the app telling you "Hey! Something happened!"
If you check your mailbox every 10 minutes to see if you have mail, that is an API call (polling). It is a waste of time.
A webhook is like the mailman ringing your doorbell only when there is a package.
In AI automation, webhooks are crucial. They trigger your workflows instantly when a payment fails, a lead signs up, or a form is submitted.
Skill 4: Logic And Control Flow
This is the brain of your automation. You need to tell the system what to do in different situations.
If/Else: If the email contains the word "Urgent," send it to Slack. If not, save it to Notion.
Loops: You have a list of 100 customers. You need the robot to do the same action for customer #1, then customer #2, all the way to #100.
Merge: Taking data from Google Sheets and data from an email and combining them into one report.
Part 4: How Does Context Engineering Improve AI Automation?
Now we get to the AI part. Most people think "Prompt Engineering" is just writing a good sentence. But for AI automation, you need "Context Engineering"
An LLM (Large Language Model) like GPT-5.2 is smart, but it has amnesia. It doesn't know who you are, what your business does, or what happened 5 minutes ago unless you tell it.
Imagine you are sending a student into an exam.
Bad Approach: You just say, "Go write a good essay." (This is a generic prompt).
Context Engineering Approach: You give the student a cheat sheet with the exact facts, the tone of voice to use, and examples of A+ essays.
You must feed the AI relevant data before asking it to do the work. Let's say you want to turn a YouTube transcript into a LinkedIn post.
Bad Prompt: "Turn this text into a LinkedIn post."
Context Engineered Prompt:
Role: You are a senior social media strategist for a B2B SaaS company. You specialize in viral storytelling.
Context: I am providing a transcript of a video about "The Future of n8n". The target audience is automation agencies.
Data: [Insert Transcript Here]
Writing Guidelines:
Use short, punchy sentences.
No hashtags in the body text.
Include a "Hook" in the first line.
Use a professional but conversational tone (Flesch-Kincaid grade level 6).
Task: Extract the 3 main takeaways from the Data and write a LinkedIn post following the Guidelines.
See the difference? In AI automation, you pass the "Data" dynamically from previous steps in your workflow. This creates consistent, high-quality results.
Part 5: How Should You Plan And Build Valuable AI Automation Systems?
A common trap is opening the workflow editor without a plan. You start dragging nodes, get confused, and end up with a mess of spaghetti wires.
Before you build, grab a pen and paper. Seriously. Draw the process out.
What is the trigger?
What data do we need?
Where does that data live?
What is the final result?
If you cannot draw it on paper, you cannot build it in n8n. I use tools like Lucidchart or Miro to map everything out. This blueprint saves hours of frustration.
Don't just automate things because it is cool. Automate things that matter. A process is worth automating if it hits at least two of these pillars:
Repetitive: Does it happen the same way 50 times a week?
Time-Consuming: Does it take a human 2 hours to do?
Error-Prone: Do humans copy-paste the wrong numbers often?
Scalable: If your business doubles, will this process break the team?
If you automate a task that happens once a year, you wasted your time. If you automate a daily report that takes an hour, you just created massive value.
Part 6: Why Are Testing And Tracking Essential For AI Automation?
Here is a hard truth: Your automation will break.
Maybe the API changes. Maybe the AI gives a weird answer. Maybe the internet goes down. This is normal. The goal of AI automation is not to build a perfect system that never breaks; it is to build a resilient system that you can fix quickly.
When you are building, try to break your own workflow. Throw bad data at it. See what happens if the email is empty.
And crucially, set up logging. Do not rely on the n8n execution history alone, as it might get cleared.
Create a simple table in Airtable or Google Sheets.
Every time the workflow runs, add a row: "Date | Workflow Name | Status | Error Message".
If it fails, have the workflow send you a Slack message immediately.
This is how you move from a hobbyist to a professional. You need to know a system failed before your client calls you to complain.
Part 7: How Can You Turn AI Automation Skills Into A Career?
If you want to sell these services, stop talking about the tech.
Your clients do not care about JSON. They do not care about nodes. They do not care about vector databases.
1. Sell The ROI (Return On Investment)

Clients care about three things:
Saving Time: "I can give your sales team 10 hours back every week."
Saving Money: "This system does the work of a $3,000/month virtual assistant for $50/month."
Making Money: "This automation follows up with leads instantly, increasing your conversion rate by 20%."
When you pitch AI automation, you are not selling software; you are selling a better business outcome.
2. Build Your Portfolio With Data
Once you deploy a system, track the results. "This workflow has processed 5,000 invoices automatically.""This agent resolved 500 support tickets without human help." This data is your proof. It turns you from a "tech guy" into a strategic partner.
Conclusion
The world of AI automation is opening up, and 2026 is going to be the year of the builders. But you don't need to be a genius coder to win. You just need to be disciplined.
Start with the basics. Get comfortable with JSON and standard workflows. Accept the frustration of learning. It means you are growing. Plan your systems on paper before you build. And always focus on the value you create, not just the tools you use.
You have the roadmap. The only thing left to do is open a blank canvas and start building.
Resources:
If you are interested in other topics and how AI is transforming different aspects of our lives or even in making money using AI with more detailed, step-by-step guidance, you can find our other articles here:
Launch Your AI Automation Agency With These 6 No-Code Skills
From Idea to AI Automation – Build Your First App in 10 Mins*
Build a Micro AI SaaS in Hours: Automate Custom Reports with Images and Voice Notes*
I Built a Web Scraper in 10 Minutes—Here’s How You Can Too!*
Master AI Marketing: Build Your 24/7 Digital Assistant Without Code!
*indicates a premium content, if any
How would you rate the quality of this AI Workflows article? 📝 |
Reply